Caspian Sea
About this schools Wikipedia selection
SOS Children have produced a selection of wikipedia articles for schools since 2005. A good way to help other children is by sponsoring a child
| Caspian Sea | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| As captured by the MODIS on the orbiting Terra satellite | |
| Coordinates | 40°0′N 51°0′E |
| Lake type | Endorheic Saline Permanent Natural |
| Primary inflows | Volga River |
| Primary outflows | Evaporation |
| Catchment area | 3,626,000 km² (1,400,000 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Azerbaijan Iran Kazakhstan Russian Federation Turkmenistan |
|
|
|
| Surface area | 371,000 km² (143,200 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 184 m (604 ft) |
| Water volume | 78,200 km3 (18,800 cu mi) |
| Residence time | 250 years |
| Surface elevation | -28 m (-92 ft) |
|
|
|
| References | |
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. It has a surface area of 371,000 square kilometers (143,244 sq mi) and a volume of 78,200 cubic kilometers (18,761 cu mi). It is an endorheic body of water (has no outflows), and lies between the southern areas of the Russian Federation and northern Iran. It has a maximum depth of about 1025 meters (3,363 ft).
It was perceived as a sea by its ancient coastal inhabitants because it is salty and seemed boundless. It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third the salinity of most seawater. According to Strabo, it is named after an ancient people called Caspians.
Geological history
Like the Black Sea and the Mediterranean, the Caspian Sea is a remnant of the Tethys Ocean. It became landlocked about 5.5 million years ago due to continental drift. The Caspian owes what reduced salinity it has to its origins as a remnant of the World Ocean. During warm and dry climatic periods, the landlocked sea has all but dried up, depositing evaporitic sediments like halite that became covered by wind-blown deposits and were sealed off as an evaporite sink when cool, wet climates refilled the basin. Due to the inflow of fresh water, the Caspian Sea is a fresh-water lake in its northern portions. It is more saline on the Iranian shore, where the catchment basin contributes little flow. Currently, the mean salinity of the Caspian is three times less than the Earth's oceans. The largely dried-up Garabogazköl embayment routinely exceeds oceanic salinity.
Geography
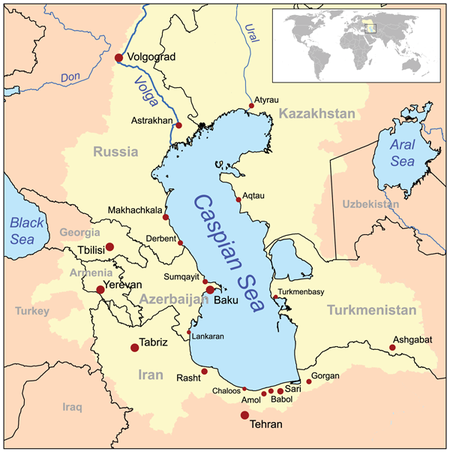
The Caspian Sea is the largest inland body of water in the world and accounts for 40 to 44 percent of the total lacustrine waters of the world. The coastlines of the Caspian are shared by Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkmenistan. The Caspian is divided into three distinct physical regions: Northern, Middle, and Southern Caspian. The North-Middle boundary is the Mangyshlak threshold, which runs through Chechen Island and Cape Tiub-Karagan. The Middle-South boundary is the Apsheron threshold, which runs through Zhiloi Island and Cape Kuuli.
The divisions between the three regions are dramatic. The Northern Caspian only includes the Caspian shelf, and is characterized as very shallow; it accounts for less than one percent of the total water volume with an average depth of only five to six meters. The sea noticeably drops off towards the Middle Caspian, where the average depth is 190 meters. The Southern Caspian is the deepest, with a depth that reaches over 1000 meters. The Middle and Southern Caspian account for 33 percent and 66 percent of the total water volume, respectively. The northern portion of the Caspian Sea typically freezes in the winter, and in the coldest winters, ice will form in the south.
Over 130 rivers provide inflow to the Caspian, with the Volga River being the largest. The Caspian also has several small islands; they are primarily located in the North and have a collective land area of roughly 2000 square kilometers. Adjacent to the North Caspian is the Caspian Depression, a low-lying region 27 meters below sea level. The Central Asian steppes stretch across the northeast coast, while the Caucasus mountains hug the Western shore. The biomes to both the north and east are characterized by cold, continental deserts. Conversely, the climate to the southwest and south are generally warm with uneven elevation due to a mix of highlands and mountain ranges; the drastic changes in climate alongside the Caspian have led to a great deal of biodiversity in the region.
Fauna

The Caspian Sea holds great numbers of sturgeon, which yield eggs that are processed into caviar. In recent years overfishing has threatened the sturgeon population to the point that environmentalists advocate banning sturgeon fishing completely until the population recovers. However, the high price of sturgeon caviar allows fisherman to afford bribes to ensure the authorities look the other way, making regulations in many locations ineffective. Caviar harvesting further endangers the fish stocks, since it targets reproductive females.
The Caspian seal, (Phoca caspica, Pusa caspica in some sources) which is endemic to the Caspian Sea, is one of very few seal species that live in inland waters (see also Baikal seal). The area has given its name to several species of birds, including the Caspian gull and the Caspian tern. There are several species and subspecies of fish endemic to the Caspian Sea, including the Kktum (also known as Caspian white fish), Caspian roach, Caspian bream (some report that the Bream occurring in the Aral Sea is the same subspecies), and a Caspian "salmon" (a subspecies of trout, Salmo trutta caspiensis). The "Caspian salmon" is critically endangered.
Hydrological characteristics

The Caspian has characteristics common to both seas and lakes. It is often listed as the world's largest lake, though it is not a freshwater lake. The Caspian became landlocked about 5.5 million years ago due to plate tectonics. The Volga River (about 80% of the inflow) and the Ural River discharge into the Caspian Sea, but it has no natural outflow other than by evaporation. Thus the Caspian ecosystem is a closed basin, with its own sea level history that is independent of the eustatic level of the world's oceans. The level of the Caspian has fallen and risen, often rapidly, many times over the centuries. Some Russian historians claim that a medieval rising of the Caspian caused the coastal towns of Khazaria, such as Atil, to flood. In 2004, the water level was -28 metres, or 28 metres (92 ft) below sea level.
Over the centuries, Caspian Sea levels have changed in synchronicity with the estimated discharge of the Volga, which in turn depends on rainfall levels in its vast catchment basin. Precipitation is related to variations in the amount of North Atlantic depressions that reach the interior, and they in turn are affected by cycles of the North Atlantic Oscillation. Thus levels in the Caspian sea relate to atmospheric conditions in the North Atlantic thousands of miles to the north and west. These factors make the Caspian Sea a valuable place to study the causes and effects of global climate change.
The last short-term sea-level cycle started with a sea-level fall of 3 m from 1929 to 1977, followed by a rise of 3 m from 1977 until 1995. Since then smaller oscillations have taken place.
Human history
Discoveries in the Huto cave near the town of Behshahr, Mazandaran south of the Caspian in Iran, suggest human habitation of the area as early as 75,000 years ago.
In classical antiquity among Greeks and Persians it was called the Hyrcanian Ocean. In Persian antiquity, as well as in modern Iran, it is known as the Khazar Sea (Persian خزر) or Mazandaran (Persian مازندران) Lake. In Turkic speaking countries it is known as the Khazar Sea. Old Russian sources call it the Khvalyn (Khvalynian) Sea after the Khvalis, inhabitants of Khwarezmia. Ancient Arabic sources refer to Bahr-e-Qazvin — the Caspian/ Qazvin Sea.
The word Caspian is derived from the name of the Caspi (Persian کاسی), an ancient people that lived to the west of the sea in Transcaucasia. Strabo wrote that "to the country of the Albanians belongs also the territory called Caspiane, which was named after the Caspian tribe, as was also the sea; but the tribe has now disappeared". Moreover, the Caspian Gate, which is the name of a region in Tehran province of Iran, is another possible piece of evidence that they migrated to the south of the sea.
Historic cities by the sea include
- Hyrcania, ancient state in the north of Iran
- Tamisheh, Mazandaran province of Iran
- Anzali, Gilan province of Iran
- Atil, Khazaria
- Khazaran
- Baku, Azerbaijan
- Sumgait, Azerbaijan
- Astara, Iran, Azerbaijan
Cities near the Caspian Sea
Major cities by the Caspian Sea:
- Astara, Azerbaijan
- Avrora, Azerbaijan
- Baku, Azerbaijan
- Bank, Azerbaijan
- Gobustan, Azerbaijan
- Kala, Azerbaijan
- Khudat, Azerbaijan
- Khachmaz, Azerbaijan
- Lankaran, Azerbaijann
- Nabran, Azerbaijan
- Oil Rocks, Azerbaijan
- Sumqayit, Azerbaijan
- Astaneh-ye Ashrafiyeh, Iran
- Astara, Iran
- Amol, Iran
- Babol, Iran
- Babolsar, Iran
- Bandar Anzali, Iran
- Bandar Torkaman, Iran
- Behshahr, Iran
- Chaloos, Iran
- Ghaem Shahr, Iran
- Gorgan, Iran
- Jooybar, Iran
- Kordkuy, Iran
- Lahijan, Iran
- Langrud, Iran
- Mahmood Abad, Iran
- Neka, Iran
- Nowshahr, Iran
- Nur, Iran
- Ramsar, Iran
- Rasht, Iran
- Rudbar, Iran
- Rudsar, Iran
- Sari, Iran
- Tonekabon, Iran
- Atyrau, Kazakhstan (formerly Guriev)
- Aqtau, Kazakhstan (formerly Shevchenko)
- Astrakhan, Russia
- Derbent, Russia
- Makhachkala, Russia
- Türkmenbaşy, Turkmenistan (formerly Krasnovodsk)
- Hazar, Turkmenistan (formerly Çeleken)
- Esenguly, Turkmenistan
- Garabogaz, Turkmenistan (formerly Bekdaş)
Islands
The Caspian Sea has numerous islands throughout. The majority of the islands are small and uninhabited islands in the North Caspian. Although the majority of the islands are uninhabited, some of them do have human settlers. Many of the islands near Azerbaijan hold significant geopolitical and economic importance, due to their oil reserves.
Bulla Island is off the coast of Azerbaijan, and holds tremendous oil reserves. Pirallahı Island, off the Azerbaijani coast as well, also possesses oil reserves; it was one of the first places in Azerbaijain that was found to have oil, and was the first place in the Caspian Sea to have sectional drilling done. Nargin was used as a former Soviet base and is the largest island in the Baku bay. Ashuradeh is situated on the easternmost end of Miankaleh peninsula to the north east of Gorgan Bay, near the Iranian coast. It was separated from the peninsula after islanders created dug a channel.
Various islands, particularly around Azerbaijan, have suffered extensive environmental damage due to oil production. Vulf, for example, has had its ecosystem severely damaged due to neighboring islands' oil production, although seals and other animals continue to inhabit it.
Existing and proposed canals
Although the Caspian Sea is endorheic, its main tributary, Volga, is connected by important shipping canals with the Don River (and thus the Black Sea) and with the Baltic Sea, with branch canals to Northern Dvina and to the White Sea.
Another Caspian tributary, the Kuma River, is connected by an irrigation canal with the Don basin as well.
Canals proposed in the past
The Main Turkmen Canal, construction of which was started in 1950, would run from Nukus on the Amu-Darya to Krasnovodsk on the Caspian Sea. It would be used not only for irrigation, but also for shipping, connecting the Amu-Darya and the Aral Sea with the Caspian. The project was abandoned soon after the death of Joseph Stalin, in favour of the Qaraqum Canal, which runs on a more southerly route and does not reach the Caspian.
Since the 1930s through the 1980s, the projects for a Pechora-Kama Canal were widely discussed, and some construction experiments using nuclear explosions were conducted in 1971. For this project, shipping was a secondary consideration; the main goal was to redirect some of the water of the Pechora River (which flows into the Arctic Ocean) via the Kama into the Volga. The goals were both irrigation and stabilizing the water level in the Caspian, which was thought to be falling dangerously fast at the time.
Eurasia Canal
In June 2007, in order to boost his oil-rich country's access to markets, Kazakhstan's President Nursultan Nazarbaev proposed a 700km link between the Caspian and Black seas. It is hoped that the "Eurasia Canal" would transform the landlocked Kazakhstan and other Central Asian countries into maritime states, enabling them to significantly increase trade volume. While the canal would traverse Russian territory, it would benefit Kazakhstan through its Caspian Sea ports. The most likely route for the canal, the officials at the Committee on Water Resources at Kazakhstan's Agriculture Ministry say, would follow the Kuma-Manych Depression, where currently a chain of rivers and lakes is already connected by an irrigation canal ( Kuma-Manych Canal). Upgrading the Volga-Don Canal would be another option.
International disputes
Negotiations related to the demarcation of the Caspian Sea have been going on for nearly a decade now among the littoral states bordering the Caspian - Azerbaijan, Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan and Iran. The status of the Caspian Sea is the key problem. There are three major issues regulated by the Caspian Sea status: access to mineral resources (oil and natural gas), access for fishing and access to international waters (through Russia's Volga river and the canals connecting it to the Black Sea and Baltic Sea). Access to the Volga River is particularly important for the landlocked states of Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan. This issue is of course sensitive to Russia, because this potential traffic will move through its territory (albeit onto the inland waterways). If a body of water is labeled as Sea then there would be some precedents and international treaties obliging the granting of access permits to foreign vessels. If a body of water is labeled merely as lake then there are no such obligations. Environmental issues are also somewhat connected to the status and borders issue.
It should be mentioned that Russia got the bulk of the former Soviet Caspian military fleet (and also currently has the most powerful military presence in the Caspian Sea). Some assets were assigned to Azerbaijan. Kazakhstan and especially Turkmenistan got a very small share because they lack major port cities.
- According to a treaty signed between Persia (Iran) and Russia, the Caspian Sea is technically a lake and it is to be divided into two sectors (Persian and Russian), but the resources (then mainly fish) would be commonly shared. The line between the two sectors was to be seen as an international border in a common lake, like Lake Albert. Also the Russian sector was sub-divided into administrative sectors of the four littoral republics.
- After the dissolution of the Soviet Union not all of the newly independent states assumed continuation of the old treaty. At first Russia and Iran announced that they would continue to adhere to the old treaty (but they don't have a common border any more, so this is practically impossible).
- Even though from a logistical point of view this should not be Iran's problem (since it is the old Soviet Union that has lost territories such as Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan), Iran has called for an equal division of the Caspian Sea among the five countries: Iran, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, and Russia. Since this has been ignored and largely suppressed by Russia’s military intimidation against Iran, now Iran intends to only recognize its old treaty (between Iran and Russia) and will challenge Russia to divide its 50% share among the three littoral states - Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan - at the International Tribune.
Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan announced that they do not consider themselves parties to this treaty.
- Later followed some proposals for common agreement between all littoral states about the status of the sea.
- Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan insisted that the sectors should be based on the median line, thus giving each state a share proportional to its Caspian coastline length. Also the sectors would form part of the sovereign territory of the particular state (thus making them international borders and also allowing each state to deal with all resources within its sector as it wishes unilaterally).
- Iran insisted that the sectors should be such that each state gets a 1/5th share of the whole Caspian Sea. This was advantageous to Iran, because it has a proportionally smaller coastline.
- Russia proposed a somewhat compromising solution: the seabed (and thus mineral resources) to be divided along sectoral lines (along the two above-described variants), the surface (and thus fishing rights) to be shared between all states (with the following variations: the whole surface to be commonly shared; each state to receive an exclusive zone and one single common zone in the centre to be shared. The second variant is deemed not practical, because of the small size of the whole sea).
- Current situation
Russia, Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan have agreed to a solution about their sectors. There are no problems between Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan, but the latter is not actively participating, so there is no agreement either. Azerbaijan is at odds with Iran over some oil fields that the both states claim. There have been occasions where Iranian patrol boats have opened fire at vessels sent by Azerbaijan for exploration into the disputed region. There are similar tensions between Azerbaijan and Turkmenistan (the latter claims that the former has pumped more oil than agreed from a field, recognized by both parties as shared). Less acute are the issues between Turkmenistan and Iran. Regardless, the southern part of the sea remains disputed.
-
- Russia and Kazakhstan signed a treaty, according to which, they divide the northern part of the Caspian Sea between them into two sectors along the median line. Each sector is an exclusive zone of its state. Thus all resources, seabed and surface are exclusive to the particular state.
- Russia and Azerbaijan signed a similar treaty about their common border.
- Kazakhstan and Azerbaijan signed a similar treaty about their common border.
- Iran doesn't recognize the bilateral agreements between the other littoral states. Iran continues to insist on a single multilateral agreement between all five littoral states (as the only way to achieve 1/5-th share).
- The position of Turkmenistan is unclear.
After Russia adopted the median line sectoral division and the three treaties already signed between some littoral states this is looking like the realistic method for regulating the Caspian borders. The Russian sector is fully defined. The Kazakhstan sector is not fully defined, but is not disputed either. Azerbaijan's, Turkmenistan's and Iran's sectors are not fully defined. It is not clear if the issue of Volga-access to vessels from Azerbaijan and Kazakhstan is covered by their agreements with Russia and also what the conditions are for Volga-access for vessels from Turkmenistan and Iran.
The Caspian littoral States meeting in 2007 signed an agreement that stops any ship not flying the national flag of a littoral state on Caspian waters.
Transportation
Several scheduled ferry services (including train ferries operate on the Caspian Sea, including: