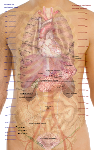
File:Surface projections of the organs of the trunk.png

| |
This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons. Information from its description page there is shown below.
Commons is a freely licensed media file repository. You can help. |
Contents |
Summary
| Description |
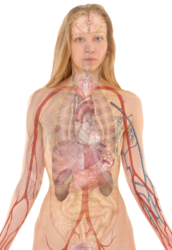
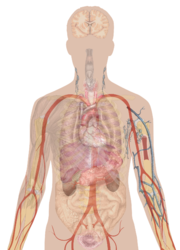
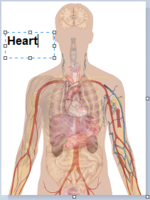
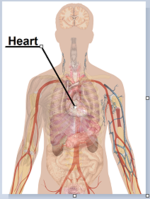
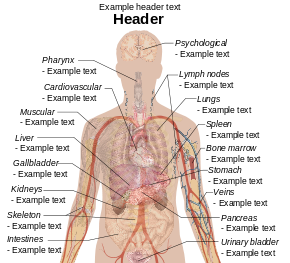
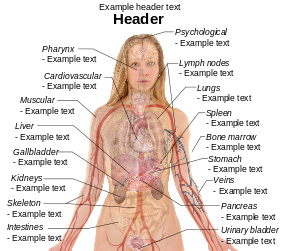
English: Surface projections of the major organs of the trunk, using the vertebral column and rib cage as main reference points of superficial anatomy. The transpyloric plane and McBurney's point are among the marked locations.
To discuss image, please see Talk:Human body diagrams |
| Date | 5 September 2010 |
| Source | All included images are in public domain. See Template:Human body diagrams for individual details. ReferencesSpinal vertebrae levels:
Gross overview of organ locations:
Locations of specific organs:
Position of the navel
Urinary tract: |
| Author | Mikael Häggström |
 |
File:Surface projections of the organs of the trunk.svg is a vector version of this file. It should be used in place of this raster image when superior. File:Surface projections of the organs of the trunk.png
For more information about vector graphics, read about Commons transition to SVG.
|
 |
Licensing
| Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
 |
I, the copyright holder of this work, release this work into the public domain. This applies worldwide. In some countries this may not be legally possible; if so: I grant anyone the right to use this work for any purpose, without any conditions, unless such conditions are required by law. Public domainPublic domainfalsefalse |
Human body diagramsMain article at: Human body diagrams Template location: Template:Human body diagrams How to derive an imageDerive directly from raster image with organsThe raster (.png format) images below have most commonly used organs already included, and text and lines can be added in almost any graphics editor. This is the easiest method, but does not leave any room for customizing what organs are shown.
Adding text and lines: Derive "from scratch"By this method, body diagrams can be derived by pasting organs into one of the "plain" body images shown below. This method requires a graphics editor that can handle transparent images, in order to avoid white squares around the organs when pasting onto the body image. Pictures of organs are found on the project's main page. These were originally adapted to fit the male shadow/silhouette.
Organs:
Derive by vector templateThe Vector templates below can be used to derive images with, for example, Inkscape. This is the method with the greatest potential. See Human body diagrams/Inkscape tutorial for a basic description in how to do this.
Examples of derived worksMore examples
Licensing
|
File usage
Metadata
| Horizontal resolution | 78.35 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 78.35 dpc |
| Software used |
|
The best way to learn
SOS Childrens Villages has brought Wikipedia to the classroom. The world's largest orphan charity, SOS Childrens Villages brings a better life to more than 2 million people in 133 countries around the globe. There are many ways to help with SOS Childrens Villages.