
15th century
Did you know...
SOS Children, an education charity, organised this selection. SOS Children works in 45 African countries; can you help a child in Africa?
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: |
|
| Decades: | 1400s 1410s 1420s 1430s 1440s 1450s 1460s 1470s 1480s 1490s |
| Categories: | Births – Deaths Establishments – Disestablishments |
The 15th century was the century which spans the Julian years 1401 to 1500.
In European history, the 15th century is seen as the bridge between the Late Middle Ages, the Early Renaissance, and the Early modern period. Many technological, social and cultural developments of the 15th century can in retrospect be seen as heralding the " European miracle" of the following centuries. In religious history, the Roman Papacy was split in two parts in Europe for decades (the so-called Western Schism), until the Council of Constance. The division of the Catholic Church and the unrest associated with the Hussite movement would give rise to the Protestant Reformation in the following century.
Constantinople, the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire, falls to emerging Ottoman Turks, forcing Western Europeans to find a new trade route. At the same time, the beginning Age of Sail allows Spanish and Portuguese explorations led to the first European sightings of the Americas (the New World) and the sea passage along Cape of Good Hope to India, in the last decade of the century. The Spanish Reconquista leads to the final fall of the Emirate of Granada by the end of the century.
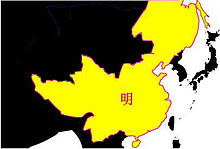
In Asia, under the rule of Yongle Emperor, who built the Forbidden City and commanded Zhenghe to explore the world overseas, Ming Dynasty's territory reached pinnacle. Tamerlane established a major empire in the Middle East and Central Asia, in order to revive the Mongolian Empire.
In Africa, the spread of Islam leads to the destruction of the Christian kingdoms of Nubia, by the end of the century leaving only Alodia (which was to collapse in 1504). The formerly vast Mali Empire teeters on the brink of collapse, under pressure from the rising Songhai Empire.
In the Americas, both the Inca Empire and the Aztec Triple Alliance reach the peak of their influence.

Events
1400s
- 1401: Dilawar Khan establishes the Malwa Sultanate in present-day central India
- 1402: Ottoman and Timurid Empires fight at the Battle of Ankara resulting in Timur's capture of Bayezid I.
- 1402: Sultanate of Malacca founded by Parameshwara.
- 1403: The Yongle Emperor moves the capital of China from Nanjing to Beijing.
- 1403: The settlement of the Canary Islands signals the beginning of the Spanish Empire.
- 1405– 1433: Zheng He of China sails through the Indian Ocean to India, Arabia, and East Africa to spread China's influence and sovereignty.
1410s
- 1410: The Battle of Grunwald is the decisive battle of the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War leading to the downfall of the Teutonic Knights.
- 1410– 1413: Foundation of St Andrews University in Scotland.
- 1414: Khizr Khan, deputised by Timur to be the governor of Multan, takes over Delhi founding the Sayyid dynasty.
- 1415: Henry the Navigator leads the conquest of Ceuta from the Moors marking the beginning of the Portuguese Empire.
- 1415: Battle of Agincourt fought between the Kingdom of England and France.
- 1415: Jan Hus is burned at the stake as a heretic at the Council of Constance.
1420s
- 1420: Construction of the Chinese Forbidden City is completed in Beijing.
- 1420– 1434: Hussite Wars in Bohemia.

.
- 1424: James I returns to Scotland after being held hostage under three Kings of England since 1406.
- 1424: Deva Raya II succeeds his father Veera Vijaya Bukka Raya as monarch of the Vijayanagara Empire.
- 1425: Catholic University of Leuven (Belgium) founded by Pope Martin V.
- 1429: Joan of Arc ends the Siege of Orléans and turns the tide of the Hundred Years' War.
1430s
- 1438: Pachacuti founds the Inca Empire.
1440s
- 1440: Eton College founded by Henry VI.
- 1440s: The Golden Horde breaks up into the Siberia Khanate, the Khanate of Kazan, the Astrakhan Khanate, the Crimean Khanate, and the Great Horde.
- 1440– 1469: Under Moctezuma I, the Aztecs become the dominant power in Mesoamerica.
- 1440: Oba Ewuare comes to power in the West African city of Benin, and turns it into an empire.
- 1441: Jan van Eyck, Flemish painter, dies
- 1441: Portuguese navigators cruise West Africa and reestablish the European slave trade with a shipment of African slaves sent directly from Africa to Portugal.
- 1443: Abdur Razzaq visits India
- 1444: The Albanian league is established in Lezha, Skanderbeg is elected leader. A war begins against Ottoman empire. An Albanian state is set up and lasts until 1479.
- 1444: Ottoman Empire under Sultan Murad II defeats the Polish and Hungarian armies under Władysław III of Poland and János Hunyadi at the Battle of Varna.
- 1445: Kazan Khanate defeats Grand Duchy of Moscow at the Battle of Suzdal
- 1446: King Sejong the Great published a hangul, the native phonetic alphabet system for the Korean language.
- 1446: Mallikarjuna Raya succeeds his father Deva Raya II as monarch of the Vijayanagara Empire
- 1449: Esen Tayisi leads an Oirat Mongol invasion of China which culminate in the capture of the Zhengtong Emperor at Battle of Tumu Fortress.
1450s
- 1450s: Machu Picchu constructed.
- 1451: Bahlul Khan Lodhi ascends the throne of the Delhi sultanate starting the Lodhi dynasty
- 1453: The Fall of Constantinople marks the end of the Byzantine Empire and the death of the last Roman Emperor Constantine XI and the beginning of the Growth of the Ottoman Empire.
- 1453: The Battle of Castillon is the last engagement of the Hundred Years' War and the first battle in European history where cannons were a major factor in deciding the battle.
- 1454– 1466: After defeating the Teutonic Knights in the Thirteen Years' War, Poland annexes Royal Prussia.
- 1455– 1485: Wars of the Roses – English civil war between the House of York and the House of Lancaster.
- 1456: Joan of Arc is posthumously acquitted of heresy by the Catholic Church, redeeming her status as the heroine of France.
- 1456: The Siege of Belgrade halts the Ottoman's advance into Europe.
1460s
- 1462: Sonni Ali Ber, the ruler of the Songhai (or Songhay) Empire, along the Niger River, conquers Mali in the central Sudan by defeating the Tuareg contingent at Tombouctou (or Timbuktu) and capturing the city. He develops both his own capital, Gao, and the main centres of Mali, Timbuktu and Djenné, into major cities. Ali Ber controls trade along the Niger River with a navy of war vessels.
- 1462: Mehmed the Conqueror is driven back by Wallachian prince Vlad III Dracula at The Night Attack.
- 1467: Uzun Hasan defeats the Black Sheep Turkoman leader Jahān Shāh.
- 1467–1615: The Sengoku period is one of civil war in Japan.
- 1469: The marriage of Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile leads to the unification of Spain.
- 1469: Matthias Corvinus of Hungary conquers some parts of Bohemia.
- 1469: Birth of Guru Nanak Dev. Beside followers of Sikhism, Guru Nanak is revered by Hindus and Muslim Sufis across the Indian subcontinent.
1470s
- 1470: The Moldavian forces under Stephen the Great defeat the Tatars of the Golden Horde at the Battle of Lipnic.
- 1471: The kingdom of Champa suffers a massive defeat by the Vietnamese king Lê Thánh Tông.
- 1474– 1477: Burgundy Wars of France, Switzerland, Lorraine and Sigismund II of Habsburg against the Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy.
- 1478: Muscovy conquers Novgorod.
- 1479: Battle of Breadfield, Matthias Corvinus of Hungary defeated the Turks.
1480s
- 1480: After the Great standing on the Ugra river, Muscovy gained independence from the Great Horde.
- 1481: Spanish Inquisition begins in practice with the first auto-da-fé.
- 1485: Matthias Corvinus of Hungary captured Vienna, Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor ran away.
- 1485: Henry VII defeats Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth. and becomes King of England.
- 1485: Ivan III of Russia conquered Tver.
- 1485: Saluva Narasimha Deva Raya drives out Praudha Raya ending the Sangama Dynasty.
- 1486: Sher Shah Suri, is born in Sasaram, Bihar.
1490s
- 1492: The death of Sunni Ali Ber left a leadership void in the Songhai Empire, and his son was soon dethroned by Mamadou Toure who ascended the throne in 1493 under the name Askia (meaning "general") Muhammad. Askia Muhammad made Songhai the largest empire in the history of West Africa. The empire went into decline, however, after 1528, when the now-blind Askia Muhammad was dethroned by his son, Askia Musa.
- 1492: Boabdil's surrender of Granada marks the end of the Spanish Reconquista and Al-Andalus.
- 1492: Jews expelled from Spain.
- 1492: Christopher Columbus landed in the Americas from Spain.
- 1494: Spain and Portugal sign the Treaty of Tordesillas and agree to divide the World outside of Europe between themselves.
- 1494–1559: The Italian Wars lead to the downfall of the Italian city-states.
- 1497– 1499: Vasco da Gama's first voyage from Europe to India and back.
- 1499: Ottoman fleet defeats Venetians at the Battle of Zonchio.
Significant people

- Abu Sa'id al-Afif, a Samaritan physician.
- Afonso de Albuquerque ( 1453–1515) was a Portuguese nobleman, naval general officer whose military and administrative activities conquered and established the Portuguese colonial empire in the Indian ocean. Generally considered as a world conquest military genius by means of his successful strategy.
- Matthias Corvinus of Hungary, Renaissance ruler ( 1443– 1490).
- George Kastrioti, Skenderbeg – Albanian Prince who resisted the Ottomans for almost 30 years ( 1443– 1468).
- Ferdinand II of Aragon, co-ruler of Spain with Isabella I of Castile and responsible with her for the unification of Spain ( 1452–1516).
- Johannes Gutenberg, European inventor of printing with movable type (c. 1398 – 1468)
- Constantine XI,The last Byzantine Emperor and Roman Emperor.He lived from 1404–1453.
- Henry the Navigator Infante Henrique, Duke of Viseu (1394– 1460); infante ( prince) of the Portuguese House of Aviz and an important figure in the early days of the Portuguese Empire, being responsible for the beginning of the European worldwide explorations.
- Henry V of England, the English King who won the famous Battle of Agincourt in 1415 (1387– 1422).

- Henry VII of England, English King and founder the Tudor dynasty ( 1457–1509).
- The Princes in the Tower, Edward V of England ( 1470– 1483?) and his brother, Richard of Shrewsbury, 1st Duke of York ( 1473– 1483?), two sons of Edward IV of England and Elizabeth Woodville.
- John Hunyadi, Regent of Kingdom of Hungary, won the Siege of Belgrade in 1456 (1387– 1456)
- Jan Hus, Bohemian religious thinker and reformer (c. 1369– 1415).
- Isabella I of Castile, co-ruler of Spain with Ferdinand II of Aragon and responsible for the unification of Spain and the discovery of the New World ( 1451–1504).
- Ivan III of Russia, Grand Duke of Moscow who ended the dominance of the Golden Horde over the Rus ( 1440- 1505)
- Joan of Arc, military commander and national heroine of France ( 1412– 1431).
- Kazimierz IV Jagiellon King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania ( 1427– 1492).
- Louis XI, King of France ( 1423– 1483).
- Mehmed II, Sultan of the Ottoman Empire and Conqueror of Constantinople ( 1432– 1481).
- Guru Nanak, founder of the Sikh Religion ( 1469).
- Sejong the Great of Joseon, a Korean monarch who developed hangul, the native Korean alphabet (1397– 1450).
- Stephen III of Moldavia, also known as Stephen the Great, ruler of Moldavia, national hero of Romanians for long resistance to the Ottomans ( 1437–1504)
- Richard III of England, last English King of the House of York, last of the House of Plantagenet ( 1452– 1485).
- Mir Chakar Khan Rind ( 1468–1565), a Baloch king.
- Vlad III Dracula, Prince of Wallachia who led the defense of his territory against the expanding Ottoman Empire ( 1431– 1476).
- Oba Ewuare, transformed the city state of Benin into the Benin Empire.
Visual artists, architects, sculptors, printmakers, illustrators

- Bartolomé Bermejo (c. 1440 – 1498), Spanish painter who adopted Dutch painting techniques and conventions.
- Pedro Berruguete (c. 1450 - 1504), Spanish painter.
- Hieronymus Bosch (c. 1450 – 1516), Early Netherlandish painter. Many of his works depict sin and human moral failings.
- Sandro Botticelli (c. 1445 – 1510), Italian painter.
- Dirk Bouts (c. 1410/ 1420 – 1475), Early Netherlandish painter.
- Filippo Brunelleschi (1377– 1446), invents one-point perspective, leads innovation in Italian architecture.
- Robert Campin (c. 1375 – 1444), the Master of Flémalle, first great master of Early Netherlandish painting.
- Petrus Christus (c. 1410/ 1420 – 1475/ 1476), Early Netherlandish painter.
- Gerard David (c. 1460 – 1523), Early Netherlandish painter and manuscript illuminator known for his brilliant use of colour.
- Albrecht Dürer ( 1471–1528) was a German painter, printmaker and theorist from Nuremberg, Germany.
- Barthélemy d'Eyck; (c. 1420 – after 1470) was an Early Netherlandish artist who worked in France and probably in Burgundy Early Netherlandish painter and manuscript illuminator. He was active between about 1440 to about 1469.
- Dionisius (c. 1440 – 1502), Russian painter
- Hubert van Eyck (c. 1366 – 1426), Flemish painter and older brother of Jan van Eyck.
- Jan van Eyck (before c. 1395 – before 1441), Early Netherlandish painter, considered one of the best Northern European painters of the 15th century.
- Juan de Flandes ( 1460–1519), Early Netherlandish painter who was active in Spain from 1496 to 1519 at the court of Isabella I of Castile.
- Jean Fouquet ( 1420– 1481) French painter of both panel painting and manuscript illumination, inventor of the portrait miniature.
- Piero della Francesca (c. 1415– 1492) Italian painter
- Nicolas Froment (c. 1435 – c. 1486), French painter.
- Lorenzo Ghiberti (1378– 1455) was an Italian artist of the early Renaissance best known for works in sculpture and metalworking.
- Hugo van der Goes (c. 1440 – 1482 or 1483), Early Netherlandish painter.
- Jean Hey (c. 1475 – c. 1505), now generally identified with the artist formerly known as the Master of Moulins, Early Netherlandish painter.
- Hans Holbein the Elder (c. 1460 – 1524), German painter, woodcut artist, illustrator of books and church window designer. He and his brother Sigismund Holbein painted religious works in the late Gothic style.
- Limbourg brothers, (Herman, Paul, and Johan; 1385– 1416), Dutch Renaissance miniature painters from the city of Nijmegen.
- Simon Marmion (c. 1425 – 1489) French, or Burgundian, painter of panels and illuminated manuscripts.
- Masaccio, (c. 1401 – 1428), Italian painter.
- Hans Memling (c. 1430 – 1494), Early Netherlandish painter, born in Germany.
- Andrei Rublev (c. 1360 – c. 1430), Russian painter.
- Enguerrand Quarton (c. 1410 – c. 1466) was a French painter and manuscript illuminator.
- Leonardo da Vinci, ( 1452–1519), Italian polymath, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, painter, sculptor, architect, botanist, musician and writer.
- Rogier van der Weyden (1399/ 1400 – 1464), considered one of the greatest exponents of Early Netherlandish painting.
See links above for Italian Renaissance painting and Renaissance sculpture.
Literature
- Leon Battista Alberti ( 1404– 1472) was an Italian author, artist, architect, poet, linguist, philosopher, and cryptographer, and general Renaissance humanist polymath.
- Joseph Albo (Hebrew: יוסף אלבו) (c. 1380 – 1444) was a Jewish philosopher and rabbi who lived in Spain. The author of Sefer ha-Ikkarim ("Book of Principles"), the classic work on the fundamentals of Judaism.
- Marsilio Ficino, Significant translator of Plato's works ( 1433– 1481).
- Iñigo López de Mendoza ( 1398 - 1458) Castilian (Spanish) politician and poet.
- John Lydgate (c. 1370 – c. 1451) was a monk and poet, born in Lidgate, Suffolk, England.
- Sir Thomas Malory (c. 1405 – March 14, 1471) was an English writer, the author or compiler of Le Morte d'Arthur.
- Pal Engjëlli ( 1416- 1470) was an Albanian Catholic clergyman, Archbishop of Durrës and Cardinal of Albania who in 1462 wrote the first known sentence in Albanian.
- Count Giovanni Pico della Mirandola ( 1463– 1494), Italian Renaissance philosopher. He is famed for the events of 1486, when at the age of twenty-three, he wrote the famous Oration on the Dignity of Man which has been called the "Manifesto of the Renaissance", and a key text of Renaissance humanism.
- Jorge Manrique (c. 1440 – 1479), Spanish poet.
- Afanasy Nikitin (? - 1472), Russian merchant, traveler and writer.
- Thomas Occleve (c. 1368 – 1426), English poet.
- Reginald Pecock (c. 1395 – 1460), was an English prelate and writer.
- Christine de Pizan, French writer (1364– 1430).
- Gil Vicente (c. 1465 – c. 1536), Portuguese poet.
- François Villon, French poet (c. 1431 – 1474).
Musicians and Composers
- Juan de Anchieta ( 1462 - 1523, Spanish composer of the Renaissance.
- Adrien Basin (c. 1457 – 1476; died after 1498), Franco-Flemish composer, singer, and diplomat of the Burgundian school of the early Renaissance.
- Gilles Binchois, (c. 1400 – 1460), Franco-Flemish composer, one of the earliest members of the Burgundian School.
- Antoine Busnois (c. 1430 – 1492), French composer and poet of the early Renaissance Burgundian School.
- Guillaume Dufay, (c. 1397 – 1474), Franco-Flemish composer and music theorist.
- John Dunstaple (c. 1390 – 1453), English composer of polyphonic music.
- Juan del Encina ( 1468 - 1530), Spanish composer, poet and playwright.
- Hayne van Ghizeghem (c. 1445 – 1472 or possibly later; New Grove says he died between 1472 and 1497), Flemish composer of the early Renaissance Burgundian School.
- Nicolas Grenon (c. 1375 – 1456), French composer of the early Renaissance.
- Robert Morton (c. 1430 – 1479), English composer of the early Renaissance.
- Johannes Ockeghem, (c. 1410 – 1497), Flemish composer.
- Francisco de Peñalosa (c. 1470 – 1528), Spanish composer of the middle Renaissance..
- Leonel Power (c. 1370 to 1385 – 1445), English composer of the late Medieval and early Renaissance eras.
- Johannes Tapissier (c. 1370 – 1408 to 1410), French composer and teacher of the late Middle Ages.
- Jacobus Vide (c. 1405 – 1433), Franco-Flemish composer of the transitional period between the medieval period and early Renaissance.
- Josquin des Prez (c. 1450 – 1521), Franco-Flemish composer of the Renaissance.
Exploration
- Johann Schiltberger (1381 – c. 1440), German traveller throughout the Middle East and Central Asia.
- Diogo de Azambuja ( 1432–1518) Portuguese explorer of the African coast.
- John Cabot (c. 1450 – 1499) – Italian explorer for England. Discovered Newfoundland and claimed it for the Kingdom of England.
- Pedro Álvares Cabral (c. 1467 – c. 1520), Portuguese navigator and explorer.
- Pêro Vaz de Caminha (c. 1450 – 1500), Portuguese explorer that accompanied Pedro Álvares Cabral in the discovery of Brazil.
- Christopher Columbus ( 1451–1506) – Italian explorer for Spain. Sailed in 1492 and discovered the " New World" of the Americas.
- Niccolò Da Conti (1395– 1469), Venetian merchant and explorer, born in Chioggia, who traveled to India and Southeast Asia.
- Bartolomeu Dias (c. 1450 – 1500) – Portuguese explorer. He sailed from Portugal and reached the Cape of Good Hope.
- Vasco da Gama reaches India for Portugal, creating the first maritime alternative for the Silk Road (c. 1469 – 1524)
- Zheng He, Chinese eunuch admiral and explorer (1371– 1433).
- João Fernandes Lavrador ( 1445?–1501) – Portuguese explorer. One of the first European's to reach Newfoundland and Labrador.
- João da Nova (c. 1460 – 1509), Portuguese explorer of the Atlantic and Indian Ocean.
- Amerigo Vespucci (c. 1454 – 1512) – Italian explorer for Spain. Sailed in 1499 and 1502. He explored the east coast of South America.
Science, invention and philosophy
- Johannes Gutenberg (c. 1400 – 1468) was a German goldsmith and printer who is credited with inventing movable type printing in Europe around 1439, and mechanical printing globally.
- Georg von Peuerbach ( 1423– 1461) was a German/Austrian astronomer and mathematician.
- Nicolaus Copernicus()Father of modern astronomy
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
List of 15th century inventions
- Renaissance affects philosophy, science and art.
- Age of Discovery begins.
- Rise of Modern English language from Middle English.
- Introduction of the noon bell in the Catholic world.
- Public banks
- Yongle Encyclopedia—over 22,000 volumes
- Hangul alphabet in Korea
- Scotch whisky
- Psychiatric hospitals
- Development of the woodcut for printing between 1400– 1450
- Movable type first used by King Taejong of Joseon— 1403 (Movable type, which allowed individual characters to be arranged to form words, was invented in China by Bi Sheng between 1041 to 1048.)
- Although pioneered earlier in Korea and by the Chinese official Wang Zhen (with tin), bronze metal movable type printing is created in China by Hua Sui in 1490.
- Johannes Gutenberg advances the printing press in Europe (c. 1455).
- Linear perspective drawing perfected by Filippo Brunelleschi 1410– 1415
- Invention of the harpsichord c. 1450
- Discovery of the Americas by Christopher Columbus 1492
Important personages
Decades and years
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||














