Somalia
Background Information
SOS Children has tried to make Wikipedia content more accessible by this schools selection. A quick link for child sponsorship is http://www.sponsor-a-child.org.uk/
| Republic of Somalia Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliya
جمهورية الصومال Jumhūriyyat as-Sūmāl |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Soomaaliyeey toosoo Somalia, Wake Up |
||||||
|
Location of Somalia (dark green)
in the Arab League (green) — [Legend] |
||||||
| Capital and largest city |
Mogadishu 2°02′N 45°21′E |
|||||
| Official languages | Somali, Arabic | |||||
| Ethnic groups | Somalis (85%), Benadiris, Bantus and other non-Somalis (15%) | |||||
| Demonym | Somali; Somalian | |||||
| Government | Coalition government | |||||
| - | President | Sharif Ahmed | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed | ||||
| - | Speaker of Parliament | Sharif Hassan Sheikh Aden | ||||
| Formation | ||||||
| - | British Somaliland | 1884 | ||||
| - | Italian Somaliland | 1889 | ||||
| - | Union and independence | 1 July 1960 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 637,657 km2 ( 43rd) 246,200 sq mi |
||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | 2010 estimate | 9,359,000 ( 87th) | ||||
| GDP ( PPP) | 2009 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $5.731 billion ( 155th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $600 ( 224th) | ||||
| HDI (2009) | N/A Error: Invalid HDI value · Not ranked |
|||||
| Currency | Somali shilling ( SOS) |
|||||
| Time zone | EAT ( UTC+3) | |||||
| - | Summer ( DST) | not observed ( UTC+3) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Calling code | 252 | |||||
| ISO 3166 code | SO | |||||
| Internet TLD | .so | |||||
| 1. | Transitional Federal Charter of the Somali Republic | |||||
Somalia (pron.: / s oʊ ˈ m ɑː l i ə / soh-MAH-lee-ə; Somali: Soomaaliya; Arabic: الصومال aṣ-Ṣūmāl), officially the Republic of Somalia ( Somali: Jamhuuriyadda Soomaaliya, Arabic: جمهورية الصومال Jumhūriyyat aṣ-Ṣūmāl) and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under communist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, the Gulf of Aden with Yemen to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, and Ethiopia to the west. With the longest coastline on the continent, its terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands.
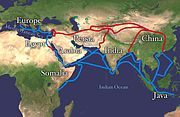
In antiquity, Somalia was an important centre for commerce with the rest of the ancient world. Its sailors and merchants were the main suppliers of frankincense, myrrh and spices, items which were considered valuable luxuries by the Ancient Egyptians, Phoenicians, Mycenaeans and Babylonians with whom the Somali people traded. According to most scholars, Somalia is most likely where the ancient Kingdom of Punt was situated. The ancient Puntites were a nation of people that had close relations with Pharaonic Egypt during the times of Pharaoh Sahure and Queen Hatshepsut. The pyramidal structures, temples and ancient houses of dressed stone littered around the country are said to date from this period. During the Middle Ages, several powerful Somali empires dominated the regional trade, including the Ajuuraan State, the Sultanate of Adal, the Warsangali Sultanate and the Gobroon Dynasty.
Somalia was never formally colonized. Muhammad Abdullah Hassan's Dervish State successfully repulsed the British Empire four times and forced it to retreat to the coastal region. Due to these successful expeditions, the Dervish State was recognized as an ally by the Ottoman and German Empires. The Turks also named Hassan Emir of the Somali nation, and the Germans promised to officially recognize any territories the Dervishes were to acquire. After a quarter of a century of holding the British at bay, the Dervishes were finally defeated in 1920 as a direct consequence of Britain's new policy of aerial bombardment. As a result of this bombardment, former Dervish territories were turned into a protectorate of Britain. Italy faced similar opposition from Somali Sultans and armies, and did not acquire full control of parts of modern Somalia until the Fascist era in late 1927. This occupation lasted until 1941, and was replaced by a British military administration. Northern Somalia would remain a protectorate, while southern Somalia became a trusteeship. The Union of the two regions in 1960 formed the Somali Republic. A civilian government was formed, and on July 20, 1961, through a popular referendum, a new constitution that had first been drafted the year before was ratified.
Due to its longstanding ties with the Arab world, Somalia was accepted in 1974 as a member of the Arab League. During the same year, the nation's former socialist administration also chaired the Organization of African Unity, the predecessor of the African Union. In 1991, the Somali Civil War broke out, which saw the collapse of the federal government. Somalia's inhabitants subsequently reverted to local forms of conflict resolution, either secular, Islamic or customary law, with a provision for appeal of all sentences. As with other previously nationalized sectors, informal providers stepped in to fill the void and replaced the former government monopoly over healthcare, with access to facilities witnessing a significant increase and general living conditions improving. Through similar grass-roots initiatives, many educational institutions were restored and newer ones were developed; several are now ranked among the 100 best universities in Africa. Additionally, a Transitional Federal Government was created in 2004, which saw the restoration of numerous national institutions, including the Military of Somalia. While it still has room for improvement, the interim government continues to reach out to both Somali and international stakeholders to help grow the administrative capacity of the Transitional Federal Institutions and to work toward eventual national elections in 2011. According to the CIA and the recently re-established Central Bank of Somalia, despite experiencing civil unrest, Somalia has also maintained a healthy informal economy, based mainly on livestock, remittance/ money transfer companies, and telecommunications. Libertarian economist Peter T. Leeson attributes this increased economic activity to the Somali traditional law (referred to as Xeer), which provides a stable environment to conduct business in.
History
Prehistory

Somalia has been inhabited since the Paleaolithic period. Cave paintings said to date back as far as 9000 BC have been found in the northern part of the country. The most famous of these is the Laas Geel complex, which contains some of the earliest known rock art on the African continent. Inscriptions have been found beneath each of the rock paintings, but archaeologists have so far been unable to decipher this form of ancient writing. During the Stone Age, the Doian culture and the Hargeisan culture flourished here with their respective industries and factories.
The oldest evidence of burial customs in the Horn of Africa comes from cemeteries in Somalia dating back to 4th millennium BC. The stone implements from the Jalelo site in northern Somalia are said to be the most important link in evidence of the universality in palaeolithic times between the East and the West.
Antiquity and classical era
Ancient pyramidal structures, tombs, ruined cities and stone walls such as the Wargaade Wall littered in Somalia are evidence of an ancient sophisticated civilization that once thrived in the Somali peninsula. The findings of archaeological excavations and research in Somalia show that this civilization had an ancient writing system that remains undeciphered, and enjoyed a lucrative trading relationship with Ancient Egypt and Mycenaean Greece since at least the second millennium BC, which supports evidence of Somalia being the ancient Land of Punt. The Puntites "traded not only in their own produce of incense, ebony and short-horned cattle, but also in goods from other neighboring regions, including gold, ivory and animal skins." According to the temple reliefs at Deir el-Bahari, the Land of Punt was ruled at that time by King Parahu and Queen Ati.
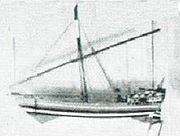
Ancient Somalis domesticated the camel somewhere between the third millennium and second millennium BC from where it spread to Ancient Egypt and North Africa. In the classical period, the city states of Mossylon, Opone, Malao, Mundus and Tabae in Somalia developed a lucrative trade network connecting with merchants from Phoenicia, Ptolemaic Egypt, Greece, Parthian Persia, Saba, Nabataea and the Roman Empire. They used the ancient Somali maritime vessel known as the beden to transport their cargo.
After the Roman conquest of the Nabataean Empire and the Roman naval presence at Aden to curb piracy, Arab and Somali merchants by agreement barred Indian ships from trading in the free port cities of the Arabian peninsula to protect the interests of Somali and Arab merchants in the extremely lucrative ancient Red Sea–Mediterranean Sea commerce. However, Indian merchants continued to trade in the port cities of the Somali peninsula, which was free from Roman interference.
The Indian merchants for centuries brought large quantities of cinnamon from Sri Lanka and Indonesia to Somalia and Arabia. This is said to have been the best kept secret of the Arab and Somali merchants in their trade with the Roman and Greek world. The Romans and Greeks believed the source of cinnamon to have been the Somali peninsula, but in reality, the highly valued product was brought to Somalia by way of Indian ships. Through collusive agreement by Somali and Arab traders, Indian/Chinese cinnamon was also exported for far higher prices to North Africa, the Near East and Europe, which made the cinnamon trade a very profitable revenue generator, especially for the Somali merchants through whose hands large quantities were shipped across ancient sea and land routes.
Birth of Islam & the Middle Ages
The history of Islam in the Horn of Africa is as old as the religion itself. The early persecuted Muslims fled to the Axumite port city of Zeila in modern day Somalia to seek protection from the Quraysh at the court of the Axumite Emperor in present day Ethiopia. Some of the Muslims that were granted protection are said to have settled in several parts of the Horn of Africa to promote the religion.
The victory of the Muslims over the Quraysh in the 7th century had a significant impact on Somalia's merchants and sailors, as their Arab trading partners had then all adopted Islam, and the major trading routes in the Mediterranean and the Red Sea came under the sway of the Muslim Caliphs. Through commerce, Islam spread amongst the Somali population in the coastal cities of Somalia. Instability in the Arabian peninsula saw several migrations of Arab families to Somalia's coastal cities, who then contributed another significant element to the growing popularity of Islam in the Somali peninsula.
Mogadishu became the centre of Islam on the East African coast, and Somali merchants established a colony in Mozambique to extract gold from the Monomopatan mines in Sofala. In northern Somalia, Adal was in its early stages a small trading community established by the newly converted Horn African Muslim merchants, who were predominantly Somali according to Arab and Somali chronicles.
The century between 1150 and 1250 marked a decisive turn in the role of Islam in Somali history. Yaqut al-Hamawi and later Ibn Said noted that the Berbers (Somalis) were a prosperous Muslim nation during that period. The Adal Sultanate was now the centre of a commercial empire stretching from Cape Guardafui to Hadiya. The Adalites then came under the influence of the expanding Horn African Ifat Sultanate, and prospered under its patronage.
The capital of Ifat was Zeila, situated in northern present-day Somalia, from where the Ifat army marched to conquer the ancient Kingdom of Shoa in 1270. This conquest ignited a rivalry for supremacy between the Christian Solomonids and the Muslim Ifatites that resulted in several devastating wars, and ultimately ended in a Solomonic victory over the Kingdom of Ifat after the death of the popular Sultan Sa'ad ad-Din II in Zeila by Dawit II. Sa'ad ad-Din II's family was subsequently given safe haven at the court of the King of Yemen, where his sons regrouped and planned their revenge on the Solomonids.
During the Age of the Ajuuraans, the sultanates and republics of Merca, Mogadishu, Barawa, Hobyo and their respective ports flourished and had a lucrative foreign commerce, with ships sailing to and coming from Arabia, India, Venetia, Persia, Egypt, Portugal and as far away as China. Vasco da Gama, who passed by Mogadishu in the 15th century, noted that it was a large city with houses several storeys high and large palaces in its centre, in addition to many mosques with cylindrical minarets.
In the 16th century, Duarte Barbosa noted that many ships from the Kingdom of Cambaya in modern-day India sailed to Mogadishu with cloth and spices, for which they in return received gold, wax and ivory. Barbosa also highlighted the abundance of meat, wheat, barley, horses, and fruit on the coastal markets, which generated enormous wealth for the merchants. Mogadishu, the centre of a thriving textile industry known as toob benadir (specialized for the markets in Egypt, among other places), together with Merca and Barawa, also served as a transit stop for Swahili merchants from Mombasa and Malindi and for the gold trade from Kilwa. Jewish merchants from the Hormuz brought their Indian textile and fruit to the Somali coast in exchange for grain and wood.
Trading relations were established with Malacca in the 15th century, with cloth, ambergris and porcelain being the main commodities of the trade. Giraffes, zebras and incense were exported to the Ming Empire of China, which established Somali merchants as leaders in the commerce between the Asia and Africa and influenced the Chinese language with the Somali language in the process. Hindu merchants from Surat and Southeast African merchants from Pate, seeking to bypass both the Portuguese blockade and Omani meddling, used the Somali ports of Merca and Barawa (which were out of the two powers' jurisdiction) to conduct their trade in safety and without interference.
Early modern era & the Scramble for Africa
In the early modern period, successor states of the Adal and Ajuuraan empires began to flourish in Somalia. These were the Gerad Dynasty, the Bari Dynasties, the Gobroon Dynasty and the Sultanate of Hobyo. They continued the tradition of castle-building and seaborne trade established by previous Somali empires.
Sultan Yusuf Mahamud Ibrahim, the third Sultan of the House of Gobroon, started the golden age of the Gobroon Dynasty. His army came out victorious during the Bardheere Jihad, which restored stability in the region and revitalized the East African ivory trade. He also received presents from and had cordial relations with the rulers of neighboring and distant kingdoms such as the Omani, Witu and Yemeni Sultans.
Sultan Ibrahim's son Ahmed Yusuf succeeded him and was one of the most important figures in 19th century East Africa, receiving tribute from Omani governors and creating alliances with important Muslim families on the East African coast. In northern Somalia, the Gerad Dynasty conducted trade with Yemen and Persia and competed with the merchants of the Bari Dynasty. The Gerads and the Bari Sultans built impressive palaces, castles and fortresses and had close relations with many different empires in the Near East.
In the late 19th century, after the Berlin conference, European powers began the Scramble for Africa, which inspired the Dervish leader Muhammad Abdullah Hassan to rally support from across the Horn of Africa and begin one of the longest colonial resistance wars ever. In several of his poems and speeches, Hassan emphasized that the British "have destroyed our religion and made our children their children" and that the Christian Ethiopians in league with the British were bent upon plundering the political and religious freedom of the Somali nation. He soon emerged as "a champion of his country's political and religious freedom, defending it against all Christian invaders."
Hassan issued a religious ordinance stipulating that any Somali national who did not accept the goal of unity of Somalia and would not fight under his leadership would be considered as kafir or gaal. He soon acquired weapons from Turkey, Sudan, and other Islamic and/or Arabian countries, and appointed ministers and advisers to administer different areas or sectors of Somalia. In addition, he gave a clarion call for Somali unity and independence, in the process organizing his forces.
Hassan's Dervish movement had an essentially military character, and the Dervish state was fashioned on the model of a Salihiya brotherhood. It was characterized by a rigid hierarchy and centralization. Though Hassan threatened to drive the Christians into the sea, he executed the first attack by launching his first major military offensive with his 1500 Dervish equipped with 20 modern rifles on the British soldiers stationed in the region.
He repulsed the British in four expeditions and had relations with the Central Powers of the Ottomans and the Germans. In 1920, the Dervish state collapsed after intensive aerial bombardments by Britain, and Dervish territories were subsequently turned into a protectorate.
The dawn of fascism in the early 1920s heralded a change of strategy for Italy, as the north-eastern sultanates were soon to be forced within the boundaries of La Grande Somalia according to the plan of Fascist Italy. With the arrival of Governor Cesare Maria De Vecchi on 15 December 1923, things began to change for that part of Somaliland known as Italian Somaliland. Italy had access to these areas under the successive protection treaties, but not direct rule.
The Fascist government had direct rule only over the Benadir territory. Fascist Italy, under Benito Mussolini, attacked Abyssinia (Ethiopia) in 1935, with an aim to colonize it. The invasion was condemned by the League of Nations, but little was done to stop it or to liberate occupied Ethiopia. On August 3, 1940, Italian troops, including Somali colonial units, crossed from Ethiopia to invade British Somaliland, and by August 14, succeeded in taking Berbera from the British.
A British force, including troops from several African countries, launched the campaign in January 1941 from Kenya to liberate British Somaliland and Italian-occupied Ethiopia and conquer Italian Somaliland. By February, most of Italian Somaliland was captured and in March, British Somaliland was retaken from the sea. The British Empire forces operating in Somaliland comprised three divisions of South African, West and East African troops. They were assisted by Somali forces led by Abdulahi Hassan with Somalis of the Isaaq, Dhulbahante, and Warsangali clans prominently participating. After World War II, the number of the Italian colonists started to decrease; their numbers had dwindled to less than 10,000 in 1960.
Independence
Following World War II, Britain retained control of both British Somaliland and Italian Somaliland as protectorates. In November 1949, the United Nations granted Italy trusteeship of Italian Somaliland, but only under close supervision and on the condition — first proposed by the Somali Youth League (SYL) and other nascent Somali political organizations, such as Hizbia Digil Mirifle Somali (HDMS) (which later became Hizbia Dastur Mustaqbal Somali) and the Somali National League (SNL), that were then agitating for independence — that Somalia achieve independence within ten years. British Somaliland remained a protectorate of Britain until 1960.
To the extent that Italy held the territory by UN mandate, the trusteeship provisions gave the Somalis the opportunity to gain experience in political education and self-government. These were advantages that British Somaliland, which was to be incorporated into the new Somali state, did not have. Although in the 1950s British colonial officials attempted, through various development efforts, to make up for past neglect, the protectorate stagnated. The disparity between the two territories in economic development and political experience would cause serious difficulties when it came time to integrate the two parts.
Meanwhile, in 1948, under pressure from their World War II allies and to the dismay of the Somalis, the British "returned" the Haud (an important Somali grazing area that was presumably 'protected' by British treaties with the Somalis in 1884 and 1886) and the Ogaden to Ethiopia, based on a treaty they signed in 1897 in which the British ceded Somali territory to the Ethiopian Emperor Menelik in exchange for his help against plundering by Somali clans.
Britain included the proviso that the Somali nomads would retain their autonomy, but Ethiopia immediately claimed sovereignty over them. This prompted an unsuccessful bid by Britain in 1956 to buy back the Somali lands it had turned over. Britain also granted administration of the almost exclusively Somali-inhabited Northern Frontier District (NFD) to Kenyan nationalists despite an informal plebiscite demonstrating the overwhelming desire of the region's population to join the newly formed Somali Republic.
A referendum was held in neighboring Djibouti (then known as French Somaliland) in 1958, on the eve of Somalia's independence in 1960, to decide whether or not to join the Somali Republic or to remain with France. The referendum turned out in favour of a continued association with France, largely due to a combined yes vote by the sizable Afar ethnic group and resident Europeans. There was also widespread vote rigging, with the French expelling thousands of Somalis before the referendum reached the polls. The majority of those who voted no were Somalis who were strongly in favour of joining a united Somalia, as had been proposed by Mahmoud Harbi, Vice President of the Government Council. Harbi was killed in a plane crash two years later. Djibouti finally gained its independence from France in 1977, and Hassan Gouled Aptidon, a Somali who had campaigned for a yes vote in the referendum of 1958, eventually wound up as Djibouti's first president (1977–1991).
British Somaliland became independent on June 26, 1960, and the former Italian Somaliland followed suit five days later. On July 1, 1960, the two territories united to form the Somali Republic, albeit within boundaries drawn up by Italy and Britain. A government was formed by Abdullahi Issa, with Aden Abdullah Osman Daar as President and Abdirashid Ali Shermarke as Prime Minister, later to become President (from 1967–1969). On July 20, 1961 and through a popular referendum, the Somali people ratified a new constitution, which was first drafted in 1960. In 1967, Muhammad Haji Ibrahim Egal became Prime Minister, a position to which he was appointed by Shermarke. Egal would later become the President of the autonomous Somaliland region in northwestern Somalia.
On October 15, 1969, while paying a visit to the northern town of Las Anod, Somalia's then President Abdirashid Ali Shermarke was shot dead by one of his own bodyguards. His assassination was quickly followed by a military coup d'état on October 21, 1969 (the day after his funeral), in which the Somali Army seized power without encountering armed opposition — essentially a bloodless takeover. The putsch was spearheaded by Major General Mohamed Siad Barre, who at the time commanded the army.
Communist rule
Alongside Barre, the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC) that assumed power after President Sharmarke's assassination was led by Major General Salaad Gabeyre Kediye and Chief of Police Jama Korshel. The SRC subsequently renamed the country the Somali Democratic Republic, dissolved the parliament and the Supreme Court, and suspended the constitution.
The revolutionary army established large-scale public works programs and successfully implemented an urban and rural literacy campaign, which helped dramatically increase the literacy rate. In addition to a nationalization program of industry and land, the new regime's foreign policy placed an emphasis on Somalia's traditional and religious links with the Arab world, eventually joining the Arab League (AL) in 1974. That same year, Barre also served as chairman of the Organization of African Unity (OAU), the predecessor of the African Union (AU).
In July 1976, Barre's SRC disbanded itself and established in its place the Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party (SRSP), a one-party government based on scientific socialism and Islamic tenets. The SRSP was an attempt to reconcile the official state ideology with the official state religion by adapting Marxist precepts to local circumstances. Emphasis was placed on the Muslim principles of social progress, equality and justice, which the government argued formed the core of scientific socialism and its own accent on self-sufficiency, public participation and popular control, as well as direct ownership of the means of production. While the SRSP encouraged private investment on a limited scale, the administration's overall direction was essentially communist.
In July 1977, the Ogaden War broke out after Barre's government sought to incorporate the predominantly Somali-inhabited Ogaden region into a Pan-Somali Greater Somalia. In the first week of the conflict, Somali armed forces took southern and central Ogaden and for most of the war, the Somali army scored continuous victories on the Ethiopian army and followed them as far as Sidamo. By September 1977, Somalia controlled 90% of the Ogaden and captured strategic cities such as Jijiga and put heavy pressure on Dire Dawa, threatening the train route from the latter city to Djibouti. After the siege of Harar, a massive unprecedented Soviet intervention consisting of 20,000 Cuban forces and several thousand Soviet experts came to the aid of Ethiopia's communist Derg regime. By 1978, the Somali troops were ultimately pushed out of the Ogaden. This shift in support by the Soviet Union motivated the Barre government to seek allies elsewhere. It eventually settled on Russia's Cold War arch-rival, the United States, which had been courting the Somali government for some time. All in all, Somalia's initial friendship with the Soviet Union and later partnership with the United States enabled it to build the largest army in Africa.
A new constitution was promulgated in 1979 under which elections for a People's Assembly were held. However, Barre's Somali Revolutionary Socialist Party politburo continued to rule. In October 1980, the SRSP was disbanded, and the Supreme Revolutionary Council was re-established in its place. By that time, the moral authority of Barre's government had collapsed. Many Somalis had become disillusioned with life under military dictatorship. The regime was weakened further in the 1980s as the Cold War drew to a close and Somalia's strategic importance was diminished. The government became increasingly totalitarian, and resistance movements, encouraged by Ethiopia, sprang up across the country, eventually leading to the Somali Civil War. Among the militia groups were the Somali Salvation Democratic Front (SSDF), United Somali Congress (USC), Somali National Movement (SNM) and the Somali Patriotic Movement (SPM), together with the non-violent political oppositions of the Somali Democratic Movement (SDM), the Somali Democratic Alliance (SDA) and the Somali Manifesto Group (SMG).
During 1990, in the capital city of Mogadishu, the residents were prohibited from gathering publicly in groups greater than three or four. Fuel shortages caused long lines of cars at petrol stations. Inflation had driven the price of pasta, (ordinary dry Italian noodles, a staple at that time), to five U.S. dollars per kilogram. The price of khat, imported daily from Kenya, was also five U.S. dollars per standard bunch. Paper currency notes were of such low value that several bundles were needed to pay for simple restaurant meals. Coins were scattered on the ground throughout the city being too low in value to be used.
A thriving black market existed in the centre of the city as banks experienced shortages of local currency for exchange. At night, the city of Mogadishu lay in darkness. The generators used to provide electricity to the city had been sold off by the government. Close monitoring of all visiting foreigners was in effect. Harsh exchange control regulations were introduced to prevent export of foreign currency and access to it was restricted to official banks, or one of three government-operated hotels.
Although no travel restrictions were placed on foreigners, photographing many locations was banned. During the day in Mogadishu, the appearance of any government military force was extremely rare. Alleged late-night operations by government authorities, however, included "disappearances" of individuals from their homes.
Somali Civil War
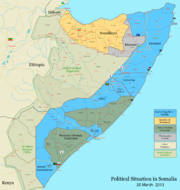
1991 was a time of great change for Somalia. President Barre was ousted by combined northern and southern clan-based forces, all of whom were backed and armed by Ethiopia. And following a meeting of the Somali National Movement and northern clans' elders, the northern former British portion of the country declared its independence as Somaliland in May 1991; although de facto independent and relatively stable compared to the tumultuous south, it has not been recognized by any foreign government.
In January 1991, President Ali Mahdi Muhammad was selected by the manifesto group as an interim state president until a conference between all stakeholders to be held in Djibouti the following month to select a national leader. However, United Somali Congress military leader General Mohamed Farrah Aidid, the Somali National Movement leader Abdirahman Ahmed Ali Tuur and the Somali Patriotic Movement leader Col Jess refused to recognize Mahdi as president.
This caused a split between the SNM, USC and SPM and the armed groups Manifesto, Somali Democratic Movement (SDM) and Somali National Alliance (SNA) on the one hand and within the USC forces. This led efforts to remove Barre who still claimed to be the legitimate president of Somalia. He and his armed supporters remained in the south of the country until mid 1992, causing further escalation in violence, especially in the Gedo, Bay, Bakool, Lower Shabelle, Lower Juba, and Middle Juba regions. The armed conflict within the USC devastated the Mogadishu area.
The civil war disrupted agriculture and food distribution in southern Somalia. The basis of most of the conflicts was clan allegiances and competition for resources between the warring clans. James Bishop, the United States last ambassador to Somalia, explained that there is "competition for water, pasturage, and... cattle. It is a competition that used to be fought out with arrows and sabers... Now it is fought out with AK-47s." The resulting famine (about 300,000 dead) caused the United Nations Security Council in 1992 to authorise the limited peacekeeping operation United Nations Operation in Somalia I (UNOSOM I). UNOSOM's use of force was limited to self-defense and, although originally welcomed by both sides, it was soon disregarded by the warring factions.
In reaction to the continued violence and the humanitarian disaster, the United States organized a military coalition with the purpose of creating a secure environment in southern Somalia for the conduct of humanitarian operations. This coalition, ( Unified Task Force or UNITAF) entered Somalia in December 1992 on Operation Restore Hope and was successful in restoring order and alleviating the famine. In May 1993, most of the United States troops withdrew and UNITAF was replaced by the United Nations Operation in Somalia II (UNOSOM II).
However, Mohamed Farrah Aidid saw UNOSOM II as a threat to his power and in June 1993 his militia attacked Pakistan Army troops, attached to UNOSOM II, (see Somalia (March 1992 to February 1996)) in Mogadishu inflicting over 80 casualties. Fighting escalated until 19 American troops and more than 1,000 civilians and militia were killed in a raid in Mogadishu during October 1993. The UN withdrew Operation United Shield in 3 March 1995, having suffered significant casualties, and with the rule of government still not restored. In August 1996, Aidid was killed in Mogadishu.
Following the outbreak of the civil war, many of Somalia's residents left the country in search of asylum. At the end of 2009, about 678,000 were under the responsibility of the UNHCR, constituting the third largest refugee group after war-afflicted Iraq and Afghanistan, respectively. Due to renewed fighting in the southern half of the country, an estimated 132,000 people left in 2009, and another 300,000 were displaced internally.
From 1800 to 1890, between 25,000–50,000 Bantu slaves from Mozambique and Tanzania are thought to have been sold from the slave market of Zanzibar to the Somali coast. Bantus are ethnically, physically, and culturally distinct from Somalis, and have remained marginalized ever since their arrival in Somalia. The number of Bantu in Somalia before the civil war is thought to be about 900,000. Since 2003, more than 12,000 Bantu refugees have been resettled in the United States. The Tanzanian government has also begun granting Bantus citizenship and land in areas of Tanzania where their ancestors are known to have been removed from.
A consequence of the collapse of governmental authority that accompanied the civil war has been the emergence of a significant problem with piracy in the waters off of the coast of Somalia. Piracy arose as a response by local fishermen from littoral towns such as Eyl, Kismayo and Harardhere to illegal fishing by foreign trawlers. An upsurge in piracy in the Gulf of Aden and the Indian Ocean has also been attributed to the effects of the December 26, 2004 tsunami that devastated local fishing fleets and washed ashore containers filled with toxic waste that had been dumped by European fishing vessels. In August 2008, a multinational coalition took on the task of combating the piracy by establishing a Maritime Security Patrol Area (MSPA) within the Gulf of Aden. Additionally, the regional Puntland government in northeastern Somalia committed itself to eradicating piracy and has so far made progress in its campaign, having apprehended numerous pirates in 2010, including a prominent leader. The autonomous region's security forces also reportedly managed to force out the pirate gangs from their traditional safe havens such as Eyl and Gar'ad, with the pirates now operating from only one main town, Harardhere. By the first half of 2010, these increased policing efforts by Puntland government authorities on land along with international naval vessels at sea reportedly contributed to a drop in pirate attacks in the Gulf of Aden from 86 a year prior to 33, forcing pirates to shift attention to other areas such as the Somali Basin and the wider Indian Ocean.
Politics
Transitional Federal Government
The Transitional Federal Government (TFG) is the current internationally recognized federal government of Somalia. It was established as one of the Transitional Federal Institutions (TFIs) of government as defined in the Transitional Federal Charter (TFC) adopted in November 2004 by the Transitional Federal Parliament (TFP). The Charter outlines a five-year mandate leading toward the establishment of a new constitution and a transition to a representative government after national elections. The TFG is the most recent attempt to restore national institutions to Somalia after the 1991 collapse of the Siad Barre regime and the ensuing Somali Civil War.
Islamic Courts Union and Ethiopian intervention
In 2006, the Islamic Courts Union (ICU), an Islamist organization, assumed control of much of the southern part of the country and promptly imposed Shari'a law. The Transitional Federal Government sought to reestablish its authority, and, with the assistance of Ethiopian troops, African Union peacekeepers and air support by the United States, managed to drive out the rival ICU and solidify its rule.
Following this defeat, the Islamic Courts Union splintered into several different factions. Some of the more radical elements, including Al-Shabaab, regrouped to continue their insurgency against the TFG and oppose the Ethiopian military's presence in Somalia. Throughout 2007 and 2008, Al-Shabaab scored military victories, seizing control of key towns and ports in both central and southern Somalia. At the end of 2008, the group had captured Baidoa but not Mogadishu. By January 2009, Al-Shabaab and other militias had managed to force the Ethiopian troops to retreat, leaving behind an under-equipped African Union peacekeeping force to assist the Transitional Federal Government's troops.
On December 29, 2008, Abdullahi Yusuf Ahmed announced before a united parliament in Baidoa his resignation as President of Somalia. In his speech, which was broadcast on national radio, Yusuf expressed regret at failing to end the country's seventeen year conflict as his government had mandated to do. He also blamed the international community for its failure to support the government, and said that the speaker of parliament would succeed him in office per the charter of the Transitional Federal Government.
Coalition government
Between May 31 and June 9, 2008, representatives of Somalia's federal government and the moderate Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) group of Islamist rebels participated in peace talks in Djibouti brokered by the former United Nations Special Envoy to Somalia, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah. The conference ended with a signed agreement calling for the withdrawal of Ethiopian troops in exchange for the cessation of armed confrontation. Parliament was subsequently expanded to 550 seats to accommodate ARS members, which then elected Sheikh Sharif Sheikh Ahmed, the former ARS chairman, to office. President Sharif shortly afterwards appointed Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, the son of slain former President Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke, as the nation's new Prime Minister.
With the help of a small team of African Union troops, the coalition government also began a counteroffensive in February 2009 to retake control of the southern half of the country. To solidify its control of southern Somalia, the TFG formed an alliance with the Islamic Courts Union, other members of the Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia, and Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufi militia. Furthermore, Al-Shabaab and Hizbul Islam, the two main Islamist groups in opposition, began to fight amongst themselves in mid-2009.
As a truce, in March 2009, Somalia's newly established coalition government announced that it would re-implement Shari'a as the nation's official judicial system. However, conflict continues in the southern and central parts of the country between government troops and extremist Islamist militants with links to al-Qaeda.
In 2009, Transparency International ranked Somalia in last place on its annual Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI), a metric that purports to show the prevalence of corruption in a country's public sector. In early 2010, the UN International Monitoring Group (IMG) also published a report claiming that the Somali government's security forces were ineffective and corrupt, and that up to half of the food aid that was destined for the conflict-stricken parts of the country was being misdirected. It also accused Somali officials of collaborating with pirates, UN contractors of helping insurgents, and the Eritrean government of still supporting rebel groups in southern Somalia despite earlier sanctions imposed on the former. Somalia's government and local businessmen, as well as United Nations officials and the Eritrean government all emphatically rejected the report's claims.
Reforms
Somalia's coalition government enacted numerous political reforms since taking office in 2009, with an emphasis on transparency and accountability. One of its first changes involved ensuring that all government institutions, which had previously been spread out in various areas throughout the country, were now based in Mogadishu, the nation's capital. The Central Bank of Somalia was also re-established, and a national plan as well as an effective anti-corruption commission were put into place. In July 2009, Somalia's Transitional Federal Government hired Pricewaterhousecoopers (PwC), one of the world's largest professional services companies and the largest of the Big Four auditing firms, to monitor development funding, with PwC now serving as a trustee of an account in Mogadishu earmarked for the security, healthcare and education sectors. This was followed in November of that year with a $2 million agreement between the government and the African Development Bank (AfDB), which saw Somalia re-engage with the AfDB after nearly two decades of interruption. The grant is aimed at providing financial and technical assistance; specifically, to develop a sound legal framework for monetary and fiscal institutions and human and institutional capacity building, as well as to establish public financial systems that are transparent.
Similarly, the autonomous Puntland region's new administration, which took office in early 2009, has also implemented numerous reforms such as the expansion and improvement of its security and judicial sectors. According to Garowe Online, to bolster the region's justice system, numerous new prosecutors, judges and other court personnel as well as additional prison guards were hired and trained. In July 2010, the Puntland Council of Ministers unanimously approved a new anti-terrorism law to more efficiently handle terror suspects and their accomplices; a special court is also expected to be established within the region's existing criminal courts system to facilitate the task. Fiscally, a transparent, budget-based public finance system was established, which has reportedly helped increase public confidence in government. In addition, a new regional constitution was drafted and later passed on June 15, 2009, which is believed to represent a significant step toward the eventual introduction of a multi-party political system to the region for the first time; such a system already exists in the adjacent Somaliland region. More modest reforms were also put into motion in the social sector, particularly in the education and healthcare fields. The regional government has hired more healthcare workers and teachers, with major plans underway for school and hospital renovations. One of the most significant new reforms enacted by the incumbent Puntland administration is the launching in May 2009 of the Puntland Agency for Social Welfare (PASWE), the first organization of its kind in Somali history. The agency provides medical, educational and counseling support to vulnerable groups and individuals such as orphans, the disabled and the blind. PASWE is overseen by a Board of Directors, which consists of religious scholars ( ulema), businesspeople, intellectuals and traditional elders.
New government
On October 14, 2010, diplomat Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed was appointed the new Prime Minister of Somalia. The former Premier Omar Abdirashid Ali Sharmarke resigned the month before following a protracted dispute with President Sharif over a proposed draft constitution.
Per the Transitional Federal Government's (TFG) Charter, Prime Minister Mohamed named a new Cabinet on November 12, 2010, which has been lauded by the international community. As had been expected, the allotted ministerial positions were significantly reduced in numbers, with only 18 administrative posts unveiled versus the previous government's bloated 39 portfolios. Only two Ministers from the previous Cabinet were reappointed: Hussein Abdi Halane, the former Minister of Finance and a well-regarded figure in the international community, was put in charge of a consolidated Ministry of Finance and Treasury; and Dr. Mohamud Abdi Ibrahim was reassigned to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. Ahlu Sunna Waljama'a, a moderate Sufi group and an important military ally of the TFG, was also accorded the key Interior and Labour ministries. The remaining ministerial positions were largely assigned to technocrats new to the Somali political arena.
While its institutions still have room for improvement, the Transitional Federal Government continues to reach out to both Somali and international stakeholders to help grow the administrative capacity of the Transitional Federal Institutions and to work toward eventual national elections in 2011, when the interim government's mandate expires.
Cities
| Largest cities or towns of Somalia . |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | City name | Region | Pop. | Rank | City name | Region | Pop. | ||
 Mogadishu |
1 | Mogadishu | Banaadir | 1,353,000 | 11 | Afgooye | Shabeellaha Hoose | 79,400 |  Bosaso |
| 2 | Hargeisa | Woqooyi Galbeed | 1,200,000 | 12 | Beledweyne | Hiran | 67,200 | ||
| 3 | Bosaso | Bari | 700,000 | 13 | Qoryoley | Shabeellaha Hoose | 62,700 | ||
| 4 | Galkacyo | Mudug | 545,000 | 14 | Garoowe | Nugaal | 57,300 | ||
| 5 | Berbera | Woqooyi Galbeed | 232,500 | 15 | Jowhar | Shabeellaha Dhexe | 57,100 | ||
| 6 | Merca | Shabeellaha Hoose | 230,100 | 16 | Bardera | Gedo | 51,300 | ||
| 7 | Jamame | Jubbada Hoose | 224,700 | 17 | Qardho | Bari | 47,400 | ||
| 8 | Kismayo | Jubbada Hoose | 183,300 | 18 | Erigavo | Sanaag | 41,000 | ||
| 9 | Baidoa | Bay | 157,500 | 19 | Luuq | Gedo | 41,000 | ||
| 10 | Burao | Togdheer | 120,400 | 20 | Borama | Awdal | 39,100 | ||
Regions and districts
Prior to the civil war, Somalia was divided into eighteen regions (gobollada, singular gobol), which were in turn subdivided into districts. The regions are:
|
1 Awdal |
7 Gedo |
13 Sanaag |
|
On a de facto basis, northern Somalia is now divided up among the quasi-independent states of Puntland and Somaliland. In Central Somalia, Galmudug is another regional entity that emerged in central Somalia just south of Puntland. The south is at least nominally controlled by the Transitional Federal Government, although it is in fact controlled by Islamist groups outside Mogadishu. Under the de facto arrangements there are now 27 regions.
Geography
Location and habitat
Somalia is bordered by Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, the Gulf of Aden with Yemen to the north, the Indian Ocean to the east, and Ethiopia to the west. Strategically located at the mouth of the Bab el Mandeb gateway to the Red Sea and the Suez Canal, the country occupies the tip of a region that, due to its resemblance on the map to a rhinoceros' horn, is commonly referred to as the Horn of Africa.
Somalia has the longest coastline on the continent, with a seaboard that stretches 3,025 kilometers. Its terrain consists mainly of plateaus, plains and highlands. The nation has a total area of 637,657 square kilometres (6.37657×1011 m2), 627,337 square kilometres (6.27337×1011 m2) of which constitutes land, with 10,320 square kilometres (1.032×1010 m2) of water. Somalia's land boundaries extend to about 2,340 kilometres (2,340,000 m); 58 kilometres (58,000 m) of that is shared with Djibouti, 682 kilometres (682,000 m) with Kenya, and 1,600 kilometres (1,600,000 m) with Ethiopia. Its maritime claims include territorial waters of 200 nautical miles (370 km; 230 mi).
In the north, a scrub-covered, semi-desert plain referred as the Guban lies parallel to the Gulf of Aden littoral. With a width of twelve kilometers in the west to as little as two kilometers in the east, the plain is bisected by watercourses that are essentially beds of dry sand except during the rainy seasons. When the rains arrive, the Guban's low bushes and grass clumps transform into lush vegetation. This coastal strip is part of the Ethiopian xeric grasslands and shrublands ecoregion.

Cal Madow is a mountain range in the northeastern part of the country. Extending from several kilometers west of the city of Bosaso to the northwest of Erigavo, it features Somalia's highest peak, Shimbiris, which sits at an elevation of about 2,416 metres (7,927 ft). The rugged east-west ranges of the Karkaar Mountains also lie to the interior of the Gulf of Aden littoral.
In the central regions, the country's northern mountain ranges give way to shallow plateaus and typically dry watercourses that are referred to locally as the Ogo. The Ogo's western plateau, in turn, gradually merges into the Haud, an important grazing area for livestock.
Somalia has only two permanent rivers, the Jubba and the Shabele, both of which begin in the Ethiopian Highlands. These rivers mainly flow southwards, with the Jubba River entering the Indian Ocean at Kismayo. The Shabele River at one time apparently used to enter the sea near Merca, but now reaches a point just southwest of Mogadishu. After that, it consists of swamps and dry reaches before finally disappearing in the desert terrain east of Jilib, near the Jubba River.
Climate
Due to Somalia's proximity to the equator, there is not much seasonal variation in its climate. Hot conditions prevail year-round along with periodic monsoon winds and irregular rainfall. Mean daily maximum temperatures range from 30 to 40 °C (86 to 104 °F), except at higher elevations and along the eastern seaboard, where the effects of a cold offshore current can be felt. In Mogadishu, for instance, average afternoon highs range from 28 °C (82 °F) to 32 °C (90 °F) in April. Some of the highest mean annual temperatures in the world have been recorded in the country; Berbera on the northwestern coast has an afternoon high that averages more than 38 °C (100 °F) from June through September. Nationally, mean daily minimums usually vary from about 15 to 30 °C (59 to 86 °F). The greatest range in climate occurs in northern Somalia, where temperatures sometimes surpass 45 °C (113 °F) in July on the littoral plains and drop below the freezing point during December in the highlands. In this region, relative humidity ranges from about 40 percent in the mid-afternoon to 85 percent at night, changing somewhat according to the season.
Unlike the climates of most other countries at this latitude, conditions in Somalia range from arid in the northeastern and central regions to semiarid in the northwest and south. In the northeast, annual rainfall is less than 4 inches (100 mm); in the central plateaus, it is about 8 to 12 inches (200 to 300 mm). The northwestern and southwestern parts of the nation, however, receive considerably more rain, with an average of 20 to 24 inches (510 to 610 mm) falling per year. Although the coastal regions are hot and humid throughout the year, the hinterland is typically dry and hot.
There are four main seasons around which pastoral and agricultural life revolve, and these are dictated by shifts in the wind patterns. From December to March is the Jilal, the harshest dry season of the year. The main rainy season, referred to as the Gu, lasts from April to June. This period is characterized by the southwest monsoons, which rejuvenate the pasture land, especially the central plateau, and briefly transform the desert into lush vegetation. From July to September is the second dry season, the Xagaa (pronounced "Hagaa"). The Dayr, which is the shortest rainy season, lasts from October to December. The tangambili periods that intervene between the two monsoons (October–November and March–May) are hot and humid.
| Climate data for Somalia | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30 (86) |
30 (86) |
40 (104) |
40 (104) |
40 (104) |
40 (104) |
40 (104) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
15 (59) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
50 (1.97) |
50 (1.97) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
40 (1.57) |
500 (19.69) |
| Source: Country Studies - Somalia | |||||||||||||
Education
Following the outbreak of the civil war in 1991, the task of running schools in Somalia was initially taken up by community education committees established in 94% of the local schools. Numerous problems had arisen with regard to access to education in rural areas and along gender lines, quality of educational provisions, responsiveness of school curricula, educational standards and controls, management and planning capacity, and financing. To address these concerns, educational policies are being developed which are aimed at guiding the scholastic process as the nation embarks on the path of reconstruction and economic development. In the autonomous Puntland region, the latter includes a gender sensitive national education policy compliant with world standards, such as those outlined in the Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) and the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW). Examples of this and other educational measures at work are the regional government's enactment of legislation aimed at securing the educational interests of girls, promoting the growth of an Early Childhood Development (ECD) program designed to reach parents and care-givers in their homes as well as in the ECD centers for 0-5 year old children, and introducing incentive packages to encourage teachers to work in remote rural areas.

The Ministry of Education is officially responsible for education in Somalia, and oversees the nation's primary, secondary, technical and vocational schools, as well as primary and technical teacher training and non-formal education. About 15% of the government's budget is allocated toward scholastic instruction. The autonomous Puntland and Somaliland macro-regions maintain their own Ministries of Education.
In 2006, Puntland was the second territory in Somalia after Somaliland to introduce free primary schools, with teachers now receiving their salaries from the Puntland administration. From 2005/2006 to 2006/2007, there was a significant increase in the number of schools in Puntland, up 137 institutions from just one year prior. During the same period, the number of classes in the region increased by 504, with 762 more teachers also offering their services. Total student enrollment increased by 27% over the previous year, with girls lagging only slightly behind boys in attendance in most regions. The highest class enrollment was observed in the northernmost Bari region, and the lowest was observed in the under-populated Ayn region. The distribution of classrooms was almost evenly split between urban and rural areas, with marginally more pupils attending and instructors teaching classes in urban areas.
Higher education in Somalia is now largely private. Several universities in the country, including Mogadishu University, have been scored among the 100 best universities in Africa in spite of the harsh environment, which has been hailed as a triumph for grass-roots initiatives. Other universities also offering higher education in the south include Benadir University, the Somalia National University, Kismayo University and the University of Gedo. In Puntland, higher education is provided by the Puntland State University and East Africa University. In Somaliland, it is provided by Amoud University, the University of Hargeisa, Somaliland University of Technology and Burao University.
Qu'ranic schools (also known as duqsi) remain the basic system of traditional religious instruction in Somalia. They provide Islamic education for children, thereby filling a clear religious and social role in the country. Known as the most stable local, non-formal system of education providing basic religious and moral instruction, their strength rests on community support and their use of locally made and widely available teaching materials. The Qu'ranic system, which teaches the greatest number of students relative to other educational sub-sectors, is often the only system accessible to Somalis in nomadic as compared to urban areas. A study from 1993 found, among other things, that about 40% of pupils in Qur'anic schools were girls. To address shortcomings in religious instruction, the Somali government on its own part also subsequently established the Ministry of Endowment and Islamic Affairs, under which Qur'anic education is now regulated.
Economy

According to the CIA and the Central Bank of Somalia, despite experiencing civil unrest, Somalia has maintained a healthy informal economy, based mainly on livestock, remittance/ money transfer companies and telecommunications. Due to a dearth of formal government statistics and the recent civil war, it is difficult to gauge the size or growth of the economy. For 1994, the CIA estimated the GDP at $3.3 billion. In 2001, it was estimated to be $4.1 billion. By 2009, the CIA estimated that the GDP had grown to $5.731 billion, with a projected real growth rate of 2.6%. According to a 2007 British Chambers of Commerce report, the private sector also grew, particularly in the service sector. Unlike the pre-civil war period when most services and the industrial sector were government-run, there has been substantial, albeit unmeasured, private investment in commercial activities; this has been largely financed by the Somali diaspora, and includes trade and marketing, money transfer services, transportation, communications, fishery equipment, airlines, telecommunications, education, health, construction and hotels. Libertarian economist Peter T. Leeson attributes this increased economic activity to the Somali customary law (referred to as Xeer), which he suggests provides a stable environment to conduct business in.
The Central Bank of Somalia indicates that the country's GDP per capita is $333, which is lower than that of Kenya at $350, but better than that of Tanzania at $280 as well as Eritrea at $190 and Ethiopia at $100. About 43% of the population live on less than 1 US dollar a day, with about 24% of those found in urban areas and 54% living in rural areas.
As with neighboring countries, Somalia's economy consists of both traditional and modern production, with a gradual shift in favour of modern industrial techniques taking root. According to the Central Bank of Somalia, about 80% of the population are nomadic or semi-nomadic pastoralists, who keep goats, sheep, camels and cattle. The nomads also gather resins and gums to supplement their income.
Agriculture is the most important economic sector. It accounts for about 65% of the GDP and employs 65% of the workforce. Livestock contributes about 40% to GDP and more than 50% of export earnings. Other principal exports include fish, charcoal and bananas; sugar, sorghum and corn are products for the domestic market. According to the Central Bank of Somalia, imports of goods total about $460 million per year, surpassing aggregate imports prior to the start of the civil war in 1991. Exports, which total about $270 million annually, have also surpassed pre-war aggregate export levels. Somalia has a trade deficit of about $190 million per year, but this is exceeded by remittances sent by Somalis in the diaspora, estimated to be about $1 billion.
With the advantage of being located near the Arabian Peninsula, Somali traders have increasingly begun to challenge Australia's traditional dominance over the Gulf Arab livestock and meat market, offering quality animals at very low prices. In response, Gulf Arab states have started to make strategic investments in the country, with Saudi Arabia building livestock export infrastructure and the United Arab Emirates purchasing large farmlands. Somalia is also a major world supplier of frankincense and myrrh.
The modest industrial sector, based on the processing of agricultural products, accounts for 10% of Somalia's GDP. Up to 14 private airline firms operating 62 aircraft now also offer commercial flights to international locations, including Daallo Airlines. With competitively priced flight tickets, these companies have helped buttress Somalia's bustling trade networks. In 2008, the Puntland government signed a multi-million dollar deal with Dubai's Lootah Group, a regional industrial group operating in the Middle East and Africa. According to the agreement, the first phase of the investment is worth Dhs 170m and will see a set of new companies established to operate, manage and build Bosaso's free trade zone and sea and airport facilities. The Bosaso Airport Company is slated to develop the airport complex to meet international standards, including a new 3.4 km runway, main and auxiliary buildings, taxi and apron areas, and security perimeters.
Prior to the outbreak of the civil war in 1991, the roughly 53 state-owned small, medium and large manufacturing firms were foundering, with the ensuing conflict destroying many of the remaining industries. However, primarily as a result of substantial local investment by the Somali diaspora, many of these small-scale plants have re-opened and newer ones have been created. The latter include fish-canning and meat-processing plants in the northern regions, as well as about 25 factories in the Mogadishu area, which manufacture pasta, mineral water, confections, plastic bags, fabric, hides and skins, detergent and soap, aluminium, foam mattresses and pillows, fishing boats, carry out packaging, and stone processing. In 2004, an $8.3 million Coca-Cola bottling plant also opened in the city, with investors hailing from various constituencies in Somalia. The robust private sector has also attracted foreign investment from the likes of General Motors and Dole Fruit.
Payment system
The Central Bank of Somalia is the official monetary authority of Somalia. In terms of financial management, it is in the process of assuming the task of both formulating and implementing monetary policy.
Owing to a lack of confidence in the local currency, the US dollar is widely accepted as a medium of exchange alongside the Somali shilling. Dollarization notwithstanding, the large issuance of the Somali shilling has increasingly fueled price hikes, especially for low value transactions. This inflationary environment, however, is expected to come to an end as soon as the Central Bank assumes full control of monetary policy and replaces the presently circulating currency introduced by the private sector.
Although Somalia has had no central monetary authority for upwards of 15 years between the outbreak of the civil war in 1991 and the subsequent re-establishment of the Central Bank of Somalia in 2009, the nation's payment system is actually fairly advanced due primarily to the widespread existence of private money transfer operators (MTO) that have acted as informal banking networks.
These remittance firms ( hawalas) have become a large industry in Somalia, with an estimated $1.6 billion USD annually remitted to the region by Somalis in the diaspora via money transfer companies. Most are credentialed members of the Somali Money Transfer Association (SOMTA), an umbrella organization that regulates the community's money transfer sector, or its predecessor, the Somali Financial Services Association (SFSA). The largest of the Somali MTOs is Dahabshiil, a Somali-owned firm employing more than 2000 people across 144 countries with branches in London and Dubai.
As the reconstituted Central Bank of Somalia fully assumes its monetary policy responsibilities, some of the existing money transfer companies are expected in the near future to seek licenses so as to develop into full-fledged commercial banks. This will serve to expand the national payments system to include formal cheques, which in turn is expected to reinforce the efficacy of the use of monetary policy in domestic macroeconomic management.
Energy
The World Bank reports that electricity is now in large part supplied by local businesses, using generators purchased abroad. By dividing Somalia's cities into specific quarters, the private sector has found a manageable method of providing cities with electricity. A customer is given a menu of choices for electricity tailored to his or her needs, such as evenings only, daytime only, 24 hour-supply or charge per lightbulb.
Somalia has untapped reserves of numerous natural resources, including uranium, iron ore, tin, gypsum, bauxite, copper, salt and natural gas. Due to its proximity to the oil-rich Gulf Arab states such as Saudi Arabia and Yemen, the nation is also believed to contain substantial unexploited reserves of oil. A survey of Northeast Africa by the World Bank and U.N. ranked Somalia second only to Sudan as the top prospective producer. American, Australian and Chinese oil companies, in particular, are excited about the prospect of finding petroleum and other natural resources in the country. An oil group listed in Sydney, Range Resources, anticipates that the Puntland province in the north has the potential to produce 5 billion barrels (790×106 m3) to 10 billion barrels (1.6×109 m3) of oil. As a result of these developments, the Somali Petroleum Company was created by the federal government.
According to surveys, uranium is also found in large quantities in the Buurhakaba region. A Brazilian company in the 1980s had invested $300 million for a uranium mine in central Somalia, but no long-term mining took place.
Additionally, the Puntland region under the Farole administration has since sought to refine the province's existing oil deal with Range Resources. The Australian oil firm, for its part, indicated that it looked forward to establishing a mutually beneficial and profitable working relationship with the region's new government.
In mid-2010, Somalia's business community also pledged to invest $1 billion in the national gas and electricity industries over the following five years. Abdullahi Hussein, the director of the just-formed Trans-National Industrial Electricity and Gas Company, predicted that the investment strategy would create 100,000 jobs, with the net effect of stimulating the local economy and discouraging unemployed youngsters from turning to vice. The new firm was established through the merger of five Somali companies from the trade, finance, security and telecommunications sectors. The first phase of the project is scheduled to start within six months of the establishment of the company, and will train youth to supply electricity to economic areas and communities. The second phase, which is slated to begin in mid-to-late 2011, will see the construction of factories in specially designated economic zones for the fishing, agriculture, livestock and mining industries.
According to the Central Bank of Somalia, as the nation embarks on the path of reconstruction, the economy is expected to not only match its pre-civil war levels, but also to accelerate in growth and development due to Somalia's untapped natural resources.
Military

Prior to the outbreak of the civil war in 1991 and the subsequent disintegration of the Armed Forces, Somalia's friendship with the Soviet Union and later partnership with the United States enabled it to build the largest army in Africa. The creation of the Transitional Federal Government in 2004 saw the re-establishment of the Military of Somalia, which now maintains a force of 10,000 troops.
The Ministry of Defense is responsible for the Armed Forces. The Somali Navy is also being re-established, with 500 Marines currently training in Mogadishu out of an expected 5,000-strong force. In addition, there are plans for the re-establishment of the Somali Air Force, with six combat and six transport planes already purchased. A new police force was also formed to maintain law and order, with the first police academy to be built in Somalia for several years opening on December 20, 2005 at Armo, 100 kilometers south of Bosaso, the commercial capital of the northeastern Puntland region. Additionally, construction began in May 2010 on a new naval base in the town of Bandar Siyada, located 25 km west of Bosaso. The new naval base is funded by the Puntland administration in conjunction with Saracen International, a UK-based security company. It will include a centre for training recruits, and a command post for the naval force.
Environment
Somalia is a semi-arid country with about 1.64% arable land. The first local environmental organizations were ECOTERRA Somalia and the Somali Ecological Society, both of which helped promote awareness about ecological concerns and mobilized environmental programs in all governmental sectors as well as in civil society. From 1971 onwards, a massive tree-planting campaign on a nationwide scale was introduced by the Siad Barre government to halt the advance of thousands of acres of wind-driven sand dunes that threatened to engulf towns, roads and farm land. By 1988, 265 hectares of a projected 336 hectares had been treated, with 39 range reserve sites and 36 forestry plantation sites established. In 1986, the Wildlife Rescue, Research and Monitoring Centre was established by ECOTERRA Intl., with the goal of sensitizing the public to ecological issues. This educational effort led in 1989 to the so-called "Somalia proposal" and a decision by the Somali government to adhere to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), which established for the first time a worldwide ban on the trade of elephant ivory.
Later, Fatima Jibrell, a prominent Somali environmental activist, mounted a successful campaign to salvage old-growth forests of acacia trees in the northeastern part of Somalia. These trees, which can grow up to 500 years old, were being cut down to make charcoal since this so-called "black gold" is highly in demand in the Arabian Peninsula, where the region's Bedouin tribes believe the acacia to be sacred. However, while being a relatively inexpensive fuel that meets a user's needs, the production of charcoal often leads to deforestation and desertification. As a way of addressing this problem, Jibrell and the Horn of Africa Relief and Development Organization (Horn Relief), an organization of which she is a co-founder and Executive Director, trained a group of adolescents to educate the public on the permanent damage that producing charcoal can create. In 1999, Horn Relief coordinated a peace march in the northeastern Puntland region of Somalia to put an end to the so-called "charcoal wars." As a result of Jibrell's lobbying and education efforts, the Puntland government in 2000 prohibited the exportation of charcoal. The government has also since enforced the ban, which has reportedly led to an 80% drop in exports of the product. Jibrell was awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize in 2002 for her efforts against environmental degradation and desertification. In 2008, she also won the National Geographic Society/ Buffett Foundation Award for Leadership in Conservation.
Following the massive tsunami of December 2004, there have also emerged allegations that after the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in the late 1980s, Somalia's long, remote shoreline was used as a dump site for the disposal of toxic waste. The huge waves which battered northern Somalia after the tsunami are believed to have stirred up tonnes of nuclear and toxic waste that was illegally dumped in the country by several European firms.
The European Green Party followed up these revelations by presenting before the press and the European Parliament in Strasbourg copies of contracts signed by two European companies — the Italian Swiss firm, Achair Partners, and an Italian waste broker, Progresso — and representatives of the then "President" of Somalia, the faction leader Ali Mahdi Mohamed, to accept 10 million tonnes of toxic waste in exchange for $80 million (then about £60 million).
According to reports by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the waste has resulted in far higher than normal cases of respiratory infections, mouth ulcers and bleeding, abdominal haemorrhages and unusual skin infections among many inhabitants of the areas around the northeastern towns of Hobyo and Benadir on the Indian Ocean coast — diseases consistent with radiation sickness. UNEP adds that the current situation along the Somali coastline poses a very serious environmental hazard not only in Somalia, but also in the eastern Africa sub-region.
Demographics
Somalia has a population of around 10 million inhabitants, about 85% of whom are ethnic Somalis. The total population according to the 1975 census was 3.3 million. Civil strife in the early 1990s greatly increased the size of the Somali diaspora, as many of the best educated Somalis left for the Middle East, Europe and North America.
Non-Somali ethnic minority groups make up the remainder of the nation's population, and are largely concentrated in the southern regions. They include Benadiri, Bravanese, Bantus, Bajuni, Ethiopians, Indians, Persians, Italians and Britons. Most Europeans left after independence.
The country's population is expanding at a growth rate of 2.809% per annum and a birth rate of 43.33 births/1,000 people. Most local residents are young, with a median age of 17.6 years; about 45% of the population is between the ages of 0–14 years, 52.5% is between the ages of 15–64 years, and only 2.5% is 65 years of age or older. The gender ratio is roughly balanced, with proportionally about as many men as women.
There is little reliable statistical information on urbanization in Somalia. However, rough estimates have been made indicating a rate of urbanization of 4.2% per annum (2005-10 est.), with many towns quickly growing into cities. As of 2008, 37% of the nation's population live in towns and cities, with the percentage rapidly increasing.
Languages
The Somali language is the official language of Somalia. It is a member of the Cushitic branch of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and its nearest relatives are the Afar and Saho languages. Somali is the best documented of the Cushitic languages, with academic studies of it dating from before 1900.
Somali dialects are divided into three main groups: Northern, Benadir and Maay. Northern Somali (or Northern-Central Somali) forms the basis for Standard Somali. Benadir (also known as Coastal Somali) is spoken on the Benadir coast from Cadaley to south of Merca, including Mogadishu, as well as in the immediate hinterland. The coastal dialects have additional phonemes which do not exist in Standard Somali. Maay is principally spoken by the Digil and Mirifle ( Rahanweyn) clans in the southern areas of Somalia.
Since Somali had long lost its ancient script, a number of writing systems have been used over the years for transcribing the language. Of these, the Somali alphabet is the most widely used, and has been the official writing script in Somalia since the government of former President of Somalia Siad Barre formally introduced it in October 1972.
The script was developed by the Somali linguist Shire Jama Ahmed specifically for the Somali language, and uses all letters of the English Latin alphabet except p, v and z. Besides Ahmed's Latin script, other orthographies that have been used for centuries for writing Somali include the long-established Arabic script and Wadaad's writing. Indigenous writing systems developed in the 20th century include the Osmanya, Borama and Kaddare scripts, which were invented by Osman Yusuf Kenadid, Sheikh Abdurahman Sheikh Nuur and Hussein Sheikh Ahmed Kaddare, respectively.
In addition to Somali, Arabic is an official national language in Somalia. Many Somalis speak it due to centuries-old ties with the Arab world, the far-reaching influence of the Arabic media, and religious education.
English is also widely used and taught. Italian used to be a major language, but its influence significantly diminished following independence. It is now most frequently heard among older generations. Other minority languages include Bravanese, a variant of the Bantu Swahili language that is spoken along the coast by the Bravanese people, as well as Kibajuni, another Swahili dialect that is the mother tongue of the Bajuni minority ethnic group.
Religion
With very few exceptions, Somalis are entirely Muslims, the majority belonging to the Sunni branch of Islam and the Shafi`i school of Islamic jurisprudence, although some are also adherents of the Shia Muslim denomination. Sufism, the mystical dimension of Islam, is also well-established, with many local jama'a ( zawiya) or congregations of the various tariiqa or Sufi orders. The constitution of Somalia likewise defines Islam as the religion of the Somali Republic, and Islamic sharia as the basic source for national legislation.
Islam entered the region very early on, as a group of persecuted Muslims had, at Prophet Muhammad's urging, sought refuge across the Red Sea in the Horn of Africa. Islam may thus have been introduced into Somalia well before the faith even took root in its place of origin.
In addition, the Somali community has produced numerous important Islamic figures over the centuries, many of whom have significantly shaped the course of Muslim learning and practice in the Horn of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and well beyond. Among these Islamic scholars is the 14th century Somali theologian and jurist Uthman bin Ali Zayla'i of Zeila, who wrote the single most authoritative text on the Hanafi school of Islam, consisting of four volumes known as the Tabayin al-Haqa’iq li Sharh Kanz al-Daqa’iq.
Christianity is a minority religion in Somalia, with no more than 1,000 practitioners in a population of over eight million inhabitants. There is one diocese for the whole country, the Diocese of Mogadishu, which estimates that there were only about 100 Catholic practitioners in Somalia in 2004.
In 1913, during the early part of the colonial era, there were virtually no Christians in the Somali territories, with only about 100-200 followers coming from the schools and orphanages of the few Catholic missions in the British Somaliland protectorate. There were also no known Catholic missions in Italian Somaliland during the same period. In the 1970s, during the reign of Somalia's then Marxist government, church-run schools were closed and missionaries sent home. There has been no archbishop in the country since 1989, and the cathedral in Mogadishu was severely damaged during the civil war.
Some non-Somali ethnic minority groups also practice animism, which represents (in the case of the Bantu) religious traditions inherited from their ancestors in southeastern Africa.
Culture
Cuisine
The cuisine of Somalia varies from region to region and consists of an exotic mixture of diverse culinary influences. It is the product of Somalia's rich tradition of trade and commerce. Despite the variety, there remains one thing that unites the various regional cuisines: all food is served halal. There are therefore no pork dishes, alcohol is not served, nothing that died on its own is eaten, and no blood is incorporated. Qaddo or lunch is often elaborate.
Varieties of bariis (rice), the most popular probably being basmati, usually serve as the main dish. Spices like cumin, cardamom, cloves, cinnamon and sage are used to aromatize these different rice dishes. Somalis serve dinner as late as 9 pm. During Ramadan, dinner is often served after Tarawih prayers – sometimes as late as 11 pm.
Xalwo or halva is a popular confection served during special occasions such as Eid celebrations or wedding receptions. It is made from sugar, corn starch, cardamom powder, nutmeg powder and ghee. Peanuts are also sometimes added to enhance texture and flavor. After meals, homes are traditionally perfumed using frankincense (lubaan) or incense (cuunsi), which is prepared inside an incense burner referred to as a dabqaad.
Music
Somalia has a rich musical heritage centered on traditional Somali folklore. Most Somali songs are pentatonic; that is, they only use five pitches per octave in contrast to a heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale. At first listen, Somali music might be mistaken for the sounds of nearby regions such as Ethiopia, Sudan or the Arabian Peninsula, but it is ultimately recognizable by its own unique tunes and styles. Somali songs are usually the product of collaboration between lyricists (midho), songwriters (lahan) and singers ('odka or "voice").
Literature
Somali scholars have for centuries produced many notable examples of Islamic literature ranging from poetry to Hadith. With the adoption of the Latin alphabet in 1972 as the nation's standard orthography, numerous contemporary Somali authors have also released novels, some of which have gone on to receive worldwide acclaim. Of these modern writers, Nuruddin Farah is probably the most celebrated. Books such as From a Crooked Rib and Links are considered important literary achievements, works which have earned Farah, among other accolades, the 1998 Neustadt International Prize for Literature. Farah Mohamed Jama Awl is another prominent Somali writer who is perhaps best known for his Dervish era novel, Ignorance is the enemy of love.
Architecture
Somali architecture is a rich and diverse tradition of engineering and designing multiple different construction types such as stone cities, castles, citadels, fortresses, mosques, temples, aqueducts, lighthouses, towers and tombs during the ancient, medieval and early modern periods in Somalia, as well as the fusion of Somalo-Islamic architecture with Occidental designs in contemporary times.
In ancient Somalia, pyramidical structures known in Somali as taalo were a popular burial style, with hundreds of these drystone monuments scattered around the country today. Houses were built of dressed stone similar to the ones in Ancient Egypt, and there are examples of courtyards and large stone walls such as the Wargaade Wall enclosing settlements.
The adoption of Islam in the early medieval era of Somalia's history brought Islamic architectural influences from Arabia and Persia, which stimulated a shift from drystone and other related materials in construction to coral stone, sundried bricks, and the widespread use of limestone in Somali architecture. Many of the new architectural designs such as mosques were built on the ruins of older structures, a practice that would continue over and over again throughout the following centuries.



![Location of Somalia (dark green)in the Arab League (green) — [Legend]](../../images/961/96146.png)